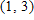An arithmetic sequence is given. Find the common difference and write out the first four terms.{sn} = {ln 6n}
A. d = ln 6; s1 = ln 6, s2 = 2 ln 6, s3 = 3 ln 6, s4 = 4 ln 6
B. d = ln 6; s1 = ln 6, s2 = ln 12, s3 = ln 18, s4 = ln 24
C. d = n ln 6; s1 = ln 6, s2 = 2 ln 6, s3 = 3 ln 6, s4 = 4 ln 6
D. d = n ln 6; s1 = ln 6, s2 = ln 12, s3 = ln 18, s4 = ln 24
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Find the indicated probability.The following table show the results of a clinical trial for an allergy drug.  What is the probability that a randomly selected person was given a placebo or improved? Round your answer to the nearest thousandth when necessary.
What is the probability that a randomly selected person was given a placebo or improved? Round your answer to the nearest thousandth when necessary.
A. 0.942 B. 0.69 C. 0.772 D. 0.17
Simplify the algebraic expression.-7(4x + 5) + 8(8x + 8)
A. -3x - 2 B. 36x + 29 C. 36x + 5 D. -63x
The concentration (in milligrams/cubic centimeter) of a certain drug in a patient's body t hr after injection is given by
?
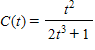
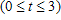

?
When is the concentration of the drug increasing and when is it decreasing?
?
A. Increasing on
B. Increasing on 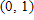
C. Decreasing on
D. The concentration of the drug is constant.
Use the graph of y = P(x) to do the following: (i) Find the x-intercepts; (ii) Solve the equation P(x) = 0; (iii) Find the zeros of P(x).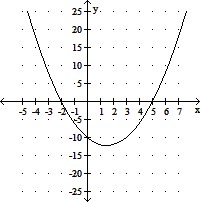
A. (i) -2, 5; (ii) -2, 5; (iii) -2, 5 B. (i) -5, 2; (ii) -5, 2; (iii) -2, 5 C. (i) -5, -2; (ii) -5, -2; (iii) -5, -2 D. (i) 5, 2; (ii) -2, 5; (iii) 5, 2