The purpose of the IMF is to:
A. provide developing countries with short-term loans and technical assistance.
B. determine monetary and fiscal policy in developing countries.
C. determine exchange rates for developing countries.
D. buy and sell the currencies of developing countries in order to stabilize their value.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
An economic recession produces
A) a decrease in cyclical unemployment. B) an increase in structural unemployment. C) a decrease in natural unemployment. D) an increase in cyclical unemployment. E) an increase in natural unemployment.
Firms in monopolistic competition would
A) persistently realize economic profits in both the short and long run. B) may realize economic profits in the long run and normal profits in the short run. C) tend to incur persistent losses in both the short and long run. D) tend to realize economic profits in the short run and normal profits in the long run.
The balance of payments constraint refers to the limits on:
A. exchange rate policy imposed by flexible exchange rates. B. currency convertibility observed in most developing countries. C. domestic macroeconomic policy, arising from a shortage of international reserves. D. macroeconomic policy resulting from IMF conditionality.
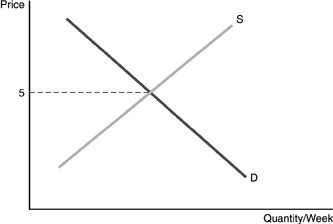 Refer to the above figure. The figure represents the market demand and supply curves for widgets in a perfectly competitive market. What statement can be made about the demand curve for an individual firm in this market?
Refer to the above figure. The figure represents the market demand and supply curves for widgets in a perfectly competitive market. What statement can be made about the demand curve for an individual firm in this market?
A. An individual firm's demand curve will be a smaller version of the market demand curve. B. An individual firm's demand curve will be horizontal at $5. C. An individual firm's demand curve will be horizontal at a price below $5. D. An individual firm's demand curve cannot be determined from the graph above.