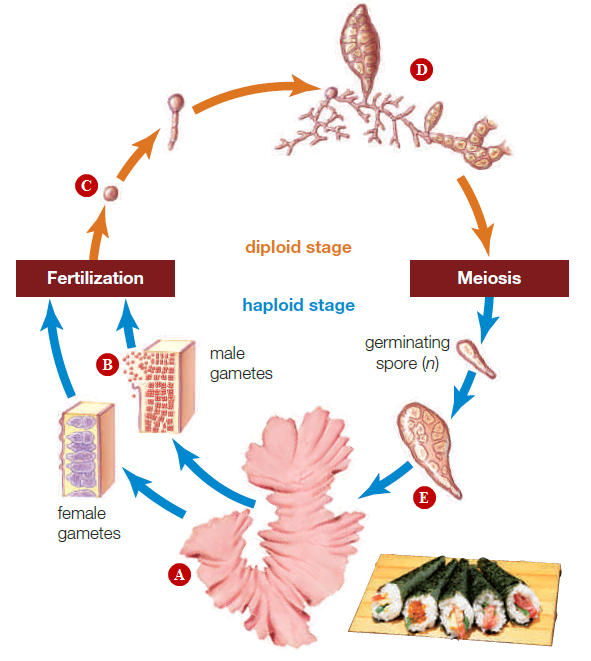
Figure 21.22
The structure labeled A is the __________.
A. gametophyte
B. sporophyte
C. sporangium
D. plant stage
E. zygote
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When lipids, phosphates, carbohydrates and RNA were placed on clay, a liposome was formed. Why was the clay an important surface for liposome formation and how is RNA associated with the liposome?
A. Clay acts as a catalyst for the formation of a liposome that can grow and divide. The RNA molecules are enclosed inside the lipid bilayer. B. Clay causes anions to stick together, while the cations are pulled from the carbohydrates. This chemical reaction causes the formation of a carbohydrate- and RNA-based membrane. C. The clay surface provides a nutritional media for the growing and dividing liposome. RNA is incorporated into the liposome as a transmembrane catalyst. D. The positively charged clay surface reacts with the negatively charged phospholipids to create a clay ball. RNA molecules adhere to the outside surface of the clay ball. E. Phospholipds react chemically with the negatively charged clay surface, creating an impermeable membrane. The RNA molecules WOULD be incorporated as part of this membrane.
Two groups of your colleagues are arguing over the amount of energy required for a beaker full of Substance X to complete an endergonic reaction. The first group insists that only the activation energy for a single reaction is necessary, which will release at least enough energy to start a second and third reaction, until all the reactants are consumed. The second group strongly disagrees, insisting that the energy required is equal to the activation energy of a single set of reactants, multiplied by the number of reactant sets in that volume of Substance X. Which group is correct?
a. Group 1 is correct, if and only if the energy released by each set of reactants is sufficient to activate a secondary reaction, after accounting for entropy. b. Group 2 is correct; the amount of energy required must equal the activation energy of all of the reactants in the beaker of Substance X. c. Group 2 is half right; endergonic reactions absorb energy, so free energy, activation energy, and entropy losses for all reactants must be included. d. Neither group is correct; endergonic reactions occur spontaneously, and the reaction has likely been completed unnoticed during this argument.
In the cAMP signal transduction pathway, a protein kinase is activated. What happens next/
a. G protein is activated. b. GDP is replaced by GTP. c. cAMP is converted to ATP. d. Adenylyl cyclase is activated. e. The protein kinase activates a cellular response.
Briefly discuss physiological mechanisms that regulate body temperature in endotherms. What will be an ideal response?