Cyclical unemployment refers to unemployment resulting from
a. a mismatch of skills
b. being in the wrong location at the wrong time
c. the time and monetary cost of finding the best job
d. climatic changes in weather affecting employment, such as agriculture and fishing
e. periodic declines in business activity.
E
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix IV. The Nash Equilibrium for the game is
Game Matrix IV
The following questions refer to the game matrix below.
Player A can play the strategies UP and DOWN and Player B can play the strategies LEFT and RIGHT.
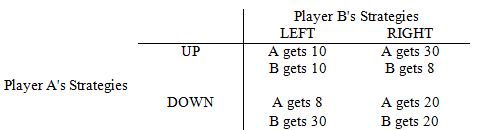
a. UP, LEFT
b. UP, RIGHT
c. DOWN, LEFT
d. DOWN, RIGHT
For a monopsony, the labor supply curve is
A) above the MCL curve. B) always below the VMP curve. C) downward sloping. D) upward sloping.
In terms of the competing claims of equality and efficiency, in the United States we have
A. chosen greater wage inequality for lower unemployment. B. chosen higher unemployment for less wage inequality. C. both greater wage inequality and higher unemployment. D. not faced a trade-off between wage inequality and unemployment. E. been able to choose both less wage inequality and lower unemployment.
If the price of inputs falls and the level of consumer indebtedness rises:
a. Price index falls, and real GDP rises. b. Price index falls, and real GDP falls. c. Price index falls, and the change in real GDP is uncertain. d. The change in price index is uncertain, and real GDP rises. e. The change in price index is uncertain, and real GDP falls.