Suppose an econometrician discovers that during the past decade, lower unemployment rates have always been accompanied by higher inflation rates. When asked how to reduce unemployment, the econometrician recommends the policy of increasing the money supply to trigger more inflation. Explain why this policy may fail to work in a world where people have rational expectations.
What will be an ideal response?
If people have rational expectations, the policy of increasing the money supply may alter their behavior and invalidate the relationship between unemployment and inflation discovered by the econometrician. For instance, when people learn that the government is increasing the money supply, they may anticipate the rise in inflation and build it into their labor contracts. Thus, the policy may create more inflation without lowering unemployment. The policy change, by leading people to change their expectations and their behavior, can eliminate the source of the tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
You might also like to view...
Each of the following is an example of an economic resource except
A. land. B. money. C. capital. D. labor.
During the period of industrialization in the U.S., real income in the agricultural sector fell
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Roughly what percentage of Americans were officially considered poor in 2012?
a. 2 percent b. 9 percent c. 15 percent d. 22 percent
Refer to the following computer output from estimating the parameters of the nonlinear modelY = aRbScTdThe computer output from the regression analysis is: 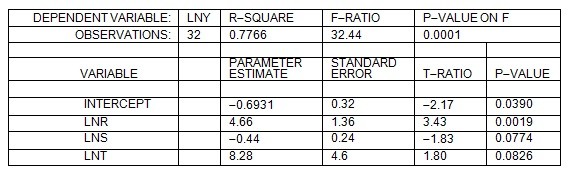 Based on the info above, if S increases by 8% (all other things constant), Y will
Based on the info above, if S increases by 8% (all other things constant), Y will
A. decrease by 4.4%. B. increase by 0.44%. C. decrease by 3.52%. D. decrease by 0.44%.