Why do some supernovae form neutron star remnants instead of white dwarfs?
What will be an ideal response?
The Chandrasekhar limit specifies that the electron degeneracy pressure that supports a white dwarf can only support an object of 1.4 solar masses or less. If the mass is greater, electrons and protons combine to make neutrons and neutrinos, and the resulting object can be supported by neutron degeneracy pressure.
You might also like to view...
If the temperature changes by 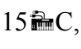 then what is the change in temperature in Fahrenheit?
then what is the change in temperature in Fahrenheit?
A. 27
B. 30
C. 32
D. 40
E. 47
Has Polaris always been the "North Star" , also known as the "Pole Star" ?
a. No, because the Earth's axis slowly changes the direction it points. b. No, because it is a young star which formed only a few hundred years ago. c. Yes, because stars position change little over many centuries. d. No, because the Milky Way blocked our line of site to it for a long time.
The possibility of life in a Europan ocean probably rests on the question of
A) whether there is enough energy in a useful form to support biology B) whether there is enough water present C) whether there is enough raw materials to build biological molecules D) the level of salinity present
The speed of a 4.0-kg object is given by v = (2t) m/s, where t is in s. At what rate is the resultant force on this object doing work at t = 1 s?
a. 48 W b. 40 W c. 32 W d. 56 W e. 16 W