Use the dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model and start with Year 1 in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium. For Year 2, graph aggregate demand, long-run aggregate supply, and short-run aggregate supply such that the condition of the economy
will induce the Federal Reserve to conduct a contractionary monetary policy. Briefly explain the condition of the economy and what the Federal Reserve is attempting to do.
What will be an ideal response?
The Federal Reserve conducts a contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation. In the graph below, the economy would move from point A in Year 1 to point B in Year 2 without any contractionary monetary policy. At point B, inflation is higher than it would be if real GDP equaled potential real GDP. The Fed would decrease the money supply and raise interest rates to slow down aggregate demand, trying to keep the economy at potential.
You might also like to view...
The American Federation of Labor was formed in 1886 as a dissident group from the
A) Knights of Labor. B) Knights of Pythias. C) Masonic Lodge. D) Knights of Columbus.
If a firm is experiencing an economic loss in the long run, then
a. it must be experiencing an accounting loss b. it should stay in business if it can cover its fixed costs c. the market must be too large d. it should exit from the industry e. price exceeds marginal cost
Consumers express self—interest when they:
A) reduce business losses. B) collect economic pro?ts. C) search for jobs with the highest wage,
Refer to the given data. Assume that before specialization and trade, Gamma and Sigma both chose production possibility "C." Now if each specializes according to comparative advantage, the gains from specialization and trade will be:
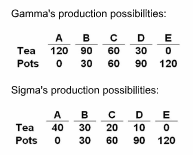
Answer the question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for Gamma and Sigma. All data are in tons.
A. 40 tons of pots.
B. 20 tons of tea and 20 tons of pots.
C. 20 tons of tea.
D. 40 tons of tea.