The Bretton Woods agreements
A. established a system of fixed exchange rates based on the free convertibility of the U.S. dollar into gold.
B. established a system of fixed exchange rates based on the gold standard.
C. permitted countries with a balance of payments deficit to make regular devaluations of their currencies.
D. established GATT to police and manage exchange rates.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to Price Ceiling. Area B + D represents
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram which shows the effects of a price ceiling. The initial price and quantity are P0 and Q0, respectively, and the price ceiling is imposed at the price P1. Assume that none of the potential deadweight loss can be avoided.
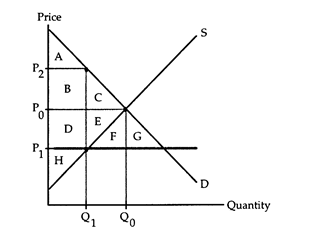
a. the deadweight loss due to the price ceiling.
b. the fall in consumers' surplus caused by the imposition of the price ceiling.
c. the value of the time and resources spent by consumers to acquire the limited supply.
d. the post-ceiling profits earned by the producers of the good.
Suppose an individual has $45,000 in annual income and considering a home that they intend to finance with a $150,000 mortgage at 4% APR 30-year fixed rate loan, the real estate taxes and insurance are $2,000 per year, auto payments are $350/month, and student loans payments are $400/month.
(1) Calculate the two qualification ratios. (2) Would this individual qualify for this loan using a standard 28/36 ratio criteria? Show all work for credit.
Budget projections for 2014-2020 indicate both higher levels of government spending and large budget deficits. According to the Keynesian view, this will lead to
a. an increase in aggregate supply during that decade. b. weak aggregate demand and a continuation of recessionary conditions. c. an increase in aggregate demand and real output. d. higher interest rates and taxes that will retard future growth.
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large tax cut will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; higher; higher B. expansionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; higher; potential D. recessionary; lower; lower