Ben is a consumer of Gouda cheese. An increase in the price of Gouda forces Ben to purchase a cheaper quality cheese. This is an example of the:
a. wealth effect
b. alternative effect.
c. income effect.
d. substitution effect.
c
You might also like to view...
If the equilibrium level of real GDP per year is greater than the full-employment level of GDP, then
A) the economy is at full employment with no price changes. B) the economy expands the level of real GDP. C) an inflationary gap occurs. D) a recessionary gap occurs.
If the number of unemployed workers in an economy is 4 million, and the size of the labor force in the economy is 16 million, the unemployment rate in the economy is:
A) 8 percent. B) 4 percent. C) 30 percent. D) 25 percent.
Consider the game depicted below. Player 1 decides between going L or R in stage 1 and 3 of the game. Player 2 decides between going l and r in stage 2 of the game.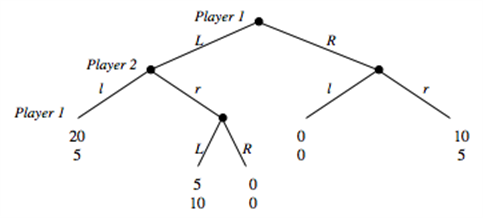
c. Identify the subgame perfect equilibrium strategies and outcome. d. Identify the Nash Equilibria that are not subgame perfect. e. For each Nash Equilibrium that is not subgame perfect, explain which parts of the Nash Equilibrium strategies are non-credible. f. Suppose you have developed a drug that can be administered without the victim being aware of it. The effect of the drug is that the victim suddenly becomes gullible and believes anything he is told. You only have 1 dose of the drug and decide to auction it off to the two players right before they play each other in the game you have analyzed so far. Each player is asked to submit a sealed bid, and the highest bidder will be sold the drug at a price equal to the highest bid. In case of a tie in bids, a coin is flipped to determine who wins and pays the price that was bid. Suppose in this part that payoffs are in terms of dollars and that bids can be made in one cent increments. Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay. Given that the players know each other's payoffs in the above game, what is the equilibrium price that you will be able to sell the drug for? (Hint: There are two possible answers.) g. In part (f), we said "Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay." Can you think of a Nash equilibrium to the auction that would end in a price of $8 if we had not made that statement in (f)? What will be an ideal response?
A group of firms that coordinate their pricing decisions is called:
A. a monopoly. B. a duopoly. C. a cartel. D. monopolistic competition.