The white dwarf that remains when our Sun dies will be mostly made of
A) hydrogen.
B) helium.
C) carbon.
D) neutrons.
C
You might also like to view...
Water flowing in a long aluminum tube is to be heated by air flowing perpendicular to the exterior of the tube. The ID of the tube is 1.85 cm and its OD is 2.3 cm. The mass flow rate of the water through the tube is 0.65 kg/s and the temperature of the water in the tube averages 30°C. The free stream velocity and ambient temperature of the air are 10 m/s and 120°C, respectively. Estimate the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger using appropriate correlations from previous chapters. State all your assumptions.
GIVEN
• Air flowing perpendicular to the exterior of an aluminum tube with water flowing within the tube
• Tube diameters
? Inside (Di) = 1.85 cm = 0.0185 m
? Outside (Do) = 2.3 cm = 0.023 m
• Mass flow rate of water (mw) = 0.65 kg/s
• Average temperature of the water (Tw) = 30°C
• Air free stream velocity (Va) = 10 m/s
• Air temperature (Ta) = 120°C FIND
• The overall heat transfer coefficient (U)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• The variation of the Prandtl number of air with temperature is negligible
• The aluminum is pure
SKETCH
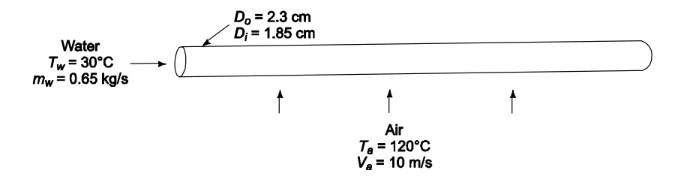
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
thermal conductivity of aluminum (kal) = 238 W/(m K) at 75°C
for water at 30°C
Density (?w) = 996 kg/m3 Thermal conductivity (kw) = 0.615 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?w) = 792 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Prw) = 5.4
for dry air at 120°C
Thermal conductivity (ka) = 0.0320 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 26.0 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
A medium-mass star evolves into a red giant because ____
a. the core expands as new fusion products collect there b. the surface of the star becomes cooler c. energy from hydrogen shell burning and helium fusion forces the outer layer to expand d. the surface of the star becomes hotter e. increased stellar winds carry large amounts of material off of the surface of the star
If there were no gravity, a cannonball fired upward at 45° would follow a straight-line path. Due to gravity, however, at the end of 3 s it is
A) 5 m below the straight line. B) 10 m below the straight line. C) 15 m below the straight line. D) 20 m below the straight line. E) more than 20 m below the straight line.
The ozone layer
a. reflects all EM waves. b. reflects high frequency radio waves. c. reflects low frequency radio waves. d. is responsible for the greenhouse effect. e. absorbs ultraviolet light in sunlight.