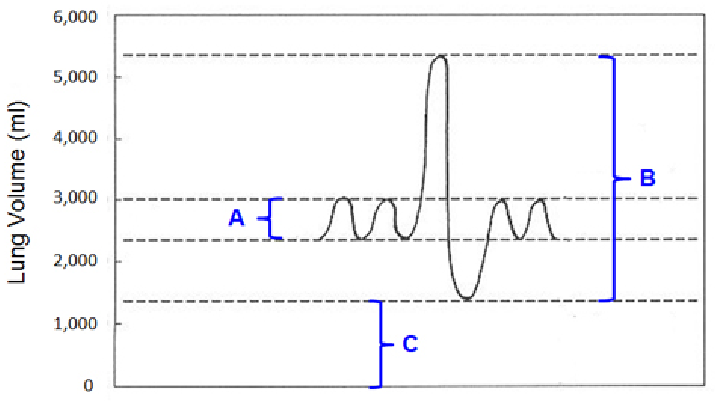
In the below graph, if Bracket A represents the tidal volume and Bracket B represents the vital capacity, respectively, of a young man, what does Bracket C represent?
A. air that is not used for gas exchange
B. air with a concentration of oxygen higher than that of air outside the body
C. anatomical dead space
D. air from a previous breath that does not mix with newly-inhaled air of the next breath
E. air that helps keep the alveoli inflated (open) after forced exhalation
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content
What do you already know about the lungs? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
E. air that helps keep the alveoli inflated (open) after forced exhalation
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· This question is asking you to interpret the function of volume of air that is not exhaled from the lungs.
What type of thinking is required?
· Apply level:
o You are being asked to take what you already know and use, or apply, it to the retention of air in the lungs.
Gather Content
What do you already know about the lungs? What other information is related to the question?
· Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli of the lungs.
· Alveoli are small sacs that must remain filled with air to maintain their shape and function.
· Tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled during quiet breathing.
· Vital capacity is the maximum exhalation that can occur after a maximum inhalation.
· Vital capacity is less than the total lung volume; some air always remains in the lungs.
Choose Answer
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
· When air is inhaled, it mixes with the air that is present in the lungs so gas exchange can occur.
· Dead anatomical space refers to space where gas exchange does not occur.
· Air inside the lungs would have an oxygen level that is equal to or less than that outside of the body.
· A volume of air is always maintained inside the lungs so that alveoli remain inflated.
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
· Apply level:
o Answering this question correctly depended on your ability to use the concept of lung volumes in a new situation. If you got an incorrect answer, did you remember that alveoli are the sites of gas exchange, or that a volume of air always remains in the lungs? Did you have trouble extending the nature of alveoli to determine the correct answer?
You might also like to view...
Echinoderms are members of the Bilateria but many members of the group (e.g., the sea stars) lack a brain, have no specialized sense organs, and have radial nerves that extend down each "arm" from a central nerve ring that surrounds the gut
What was a likely selective pressure in the evolution of this type of nervous system? A. ability to move forward B. role as a predator in the ecosystem C. multicellularity D. possession of an endoskeleton of calcium carbonate E. None of the above.
Which information is most useful?
What will be an ideal response?
Which are assemblages of abiotically produced polymers?
a. ribozymes b. stromatolites c. protobionts d. endosymbionts e. polyribosomes
Which of the following will bind to the active site of an enzyme?
A) Competitive inhibitor only B) Noncompetitive inhibitor only C) Allosteric inhibitor only D) Substrate only E) Both substrate and competitive inhibitor