At the current price of a good, Al's consumer surplus equals 8, and Ben's consumer surplus equals 15. By using two-part pricing, a monopolist could increase his profit by
A) 8.
B) 16.
C) 15.
D) 30.
B
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 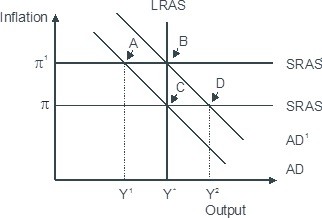
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
"Opportunity cost" is
A) the monetary cost of one's actions. B) the objective cost of one's actions. C) the regret one feels when making a sacrifice. D) the value one places on the item, project, or plan he has chosen to pursue. E) none of the above.
If the government institutes a specific tax for a good
A) the producer simply passes the entire tax on to the consumer. B) the producer must absorb the entire tax. C) the producer can generally only pass part of the tax onto the consumer. D) the equilibrium price drops.
Holding the total output constant, the rate at which one input X may be substituted for another input Y in a production process is:
a. the slope of the isoquant curve b. the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS) c. equal to MPx/MPy d. all of the above e. none of the above