Refer to Table 15-4. What is the amount of the deadweight loss generated by Shakti when it produces the monopoly output?
A) $124 B) $42 C) $36 D) $12
D
You might also like to view...
Suppose that last year the unemployment rate was 5 percent and the inflation rate was 2.5 percent. If the natural rate of unemployment is 5 percent, how do you expect inflation to change?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points D and E on their production possibilities frontier?
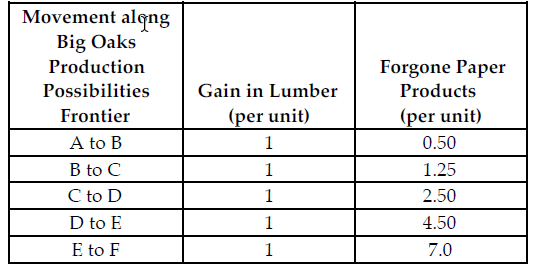
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $22.50
B) $4.50
C) $9
D) $10.50
The two groups that benefit the most from quotas are
A) the importers who have the right to import the restricted good and the domestic producers of the restricted good. B) the domestic consumers of the restricted good and the domestic producers of the restricted good. C) the domestic consumers of the restricted good and the foreign producers of the restricted good. D) the importers who have the right to import the restricted good and the domestic consumers of the restricted good.
In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will:
A. not affect the C + I g + X n line. B. shift the C + I g + X n line upward by an amount equal to T. C. shift the C + I g + X n line downward by an amount equal to T. D. shift the C + I g + X n line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC.