Refer to the graphs above. Suppose a firm is currently producing 500 computers per week and charging a price of $1000. What happens to the firm's inventory of computers if there is a negative demand shock and prices are flexible?
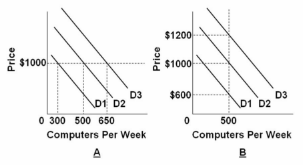
A.
The firm's inventories will not change
B.
The firm's inventories will increase by 200 computers per week
C.
The firm's inventories will decrease by 150 computers per week
D.
The firm's inventories will increase by 350 computers per week
A.
The firm's inventories will not change
You might also like to view...
At full employment,
A) the inflation rate is zero. B) the inflation rate must equal the natural unemployment rate. C) the unemployment rate is zero. D) real GDP exceeds potential GDP. E) the unemployment rate is equal to the natural unemployment rate.
If the nominal exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Thai baht (baht per dollar) is lower than the relative purchasing power between the two countries, which of the following would be true?
A) Purchasing power parity predicts that the value of the dollar will fall as traders take advantage of profit opportunities. B) Purchasing power parity predicts that the baht is undervalued as traders take advantage of profit opportunities. C) There are opportunities for profit by purchasing goods in the United States and selling them in Thailand. D) There are no opportunities for profit by purchasing goods in one country and selling them in the other.
With the assumption that some voluntary exchanges that would make both parties better off are somehow being blocked, we have the basis for a ________ macroeconomic model, such as those constructed by ________ economists
A) non-market-clearing, New Keynesian B) non-market-clearing, New Classical C) market-clearing, New Keynesian D) market-clearing, New Classical
A price floor in a perfectly competitive market
a. creates more harm for sellers than gain for buyers b. is effective only it is set at the equilibrium price c. is a Pareto improvement d. can turn an inefficient outcome into an efficient outcome e. creates more harm for buyers than gain for sellers