What is the timeline for the U.S. federal budget each year? When does a fiscal year begin and end?
What will be an ideal response?
Consider the budget for 2015 as an example in answering this question. In February 2014 the president proposes a budget to Congress. Then, from February until October 1, 2014, the Congress debates the budget, amends it, and eventually passes the necessary budget bills. The president then signs or vetoes the budget bills that were presented to him. When the president vetoes bills, the Congress may over-ride the veto or pass other bills acceptable to the president. Fiscal year 2015 begins on October 1, 2014 and runs until September 30, 2015 . During this year the Congress may pass—and the president may sign—supplementary bills. Then, after the fiscal year ends, accounts are prepared and the "official" amounts of outlays, receipts, and budget deficit or surplus are reported.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not a function of government?
a. promotion of competition b. stabilization to achieve the macroeconomic goals c. redistribution of income through taxation and transfer payments d. production of public goods e. providing the economy's private goods
The budget constraint shown below is consistent with a pricing strategy that involves a 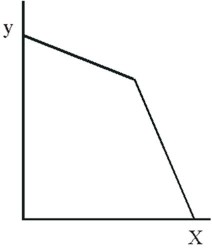
A. price increase of X for large quantities. B. price reduction of X for large quantities purchased. C. constant price of X for all quantities purchased. D. price change of X and a nominal income increase for the consumer.
The monopolistic competitor
A. may make a profit in the short run but not in the long run. B. may make a profit in the long run but not in the short run. C. may make a profit in both the short run and the long run. D. may make a profit in neither the short run nor the long run.
A legal organization of a firm where the business is owned by one individual who makes the business decisions, receives all the profits, and is legally responsible for the debts of the firm is a(n)
A) corporation. B) entrepreneur. C) proprietorship. D) partnership.