When a person dies, the body often experiences rigor mortis. In this condition, it is as if the muscles
have become inflexible and it is very difficult to manipulate the joints. Why does this occur? What will be an ideal response?
In considering the molecular mechanism of muscular contraction, you will note that for the myosin
heads to release the actin (thus breaking the cross-bridge) it is necessary for ATP to bind the myosin.
In a dead person, no ATP is produced and the cross-bridges become fixed. Thus, while the muscle is
not actively contracting it does become fixed and the body will feel stiff.
You might also like to view...
What process best characterizes Ca2+ movement from the cytosol (low Ca2+ concentration) into the endoplasmic reticulum (high Ca2+ concentration)?
A. Calcium movement is spontaneous. B. Calcium movement involves active transport. C. Calcium movement occurs by facilitated diffusion using a transporter protein. D. Calcium movement does not require energy. E. Calcium movement occurs by passive diffusion.
Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6022 yellow and 2001 green (8023 total)
The allele for green seeds has what relationship to the allele for yellow seeds? A) dominant B) incomplete dominant C) recessive D) codominant
Development of the human embryo's heart begins in the ________ week.
A. 16th B. 6th C. 1st D. 3rd E. 24th
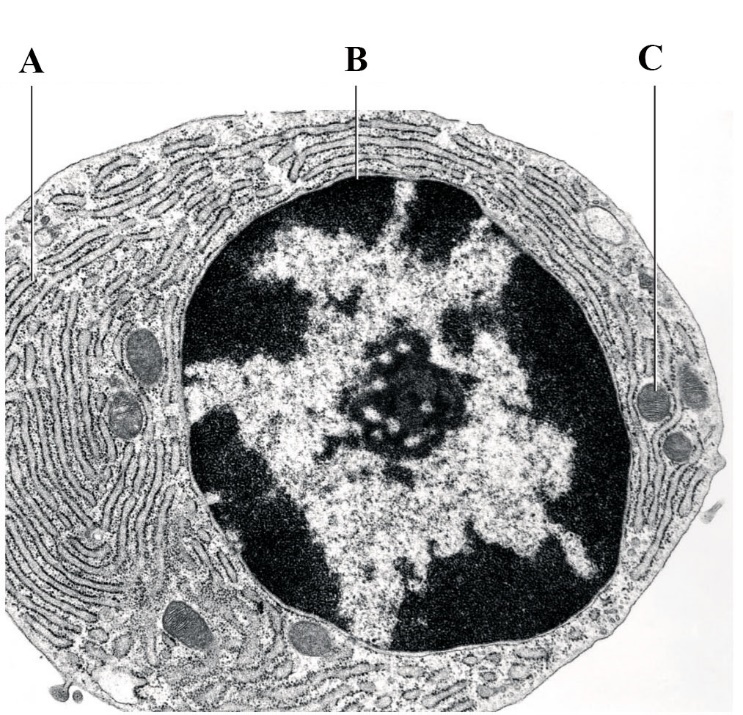
A. a nucleus B. a Golgi body C. endoplasmic reticulum D. a vacuole E. a nucleoid