Which of the following membranes can give rise to a viral envelope?
A. the nuclear membrane
B. the cytoplasmic membrane
C. the endoplasmic reticulum
D. the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes
E. the nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
The Greek word oikos means
(a) environment. (b) habitat. (c) house. (d) community.
__________ is one form of learning that happens only during a sensitive period early in life. Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
Which statement is the correct interpretation of the graph?
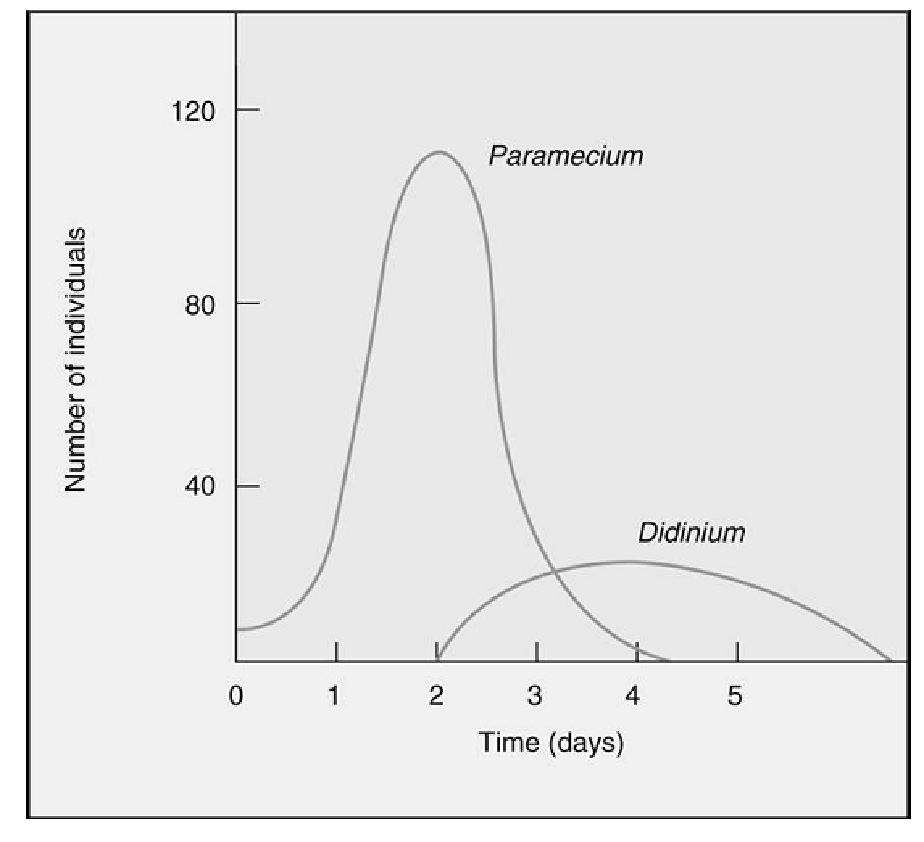
A. The population of Didinium goes extinct with the addition of Paramecium on day 4.
B. The population of Didinium continues to increase and remains high even after the extinction of the Paramecium.
C. The population of Paramecium goes extinct with the addition of Didinium on day 8.
D. The population of Didinium increased but then went extinct after the population of Paramecium went extinct.
E. The population of Didinium is able to increase at the expense of the Paramecium population. After a brief period both populations are able to coexist.
Clarify question:
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content:
What do you already know about the relationship between the two species? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer:
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflection on Process:
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Which of the following is NOT an adaptation of plants to life on land?
A. vascular system (in most plants) to move water internally B. waxy cuticle on leaves to prevent drying out C. waxy cuticle on roots to prevent drying out D. protection of the embryo from drying out