Suppose a risk-neutral competitive firm must produce output before the market price is known. If the uncertain price is given by p = p* + e, where e is a random term with an expected value of zero, a competitive firm should shut down in the short run if:
A. p* < AFC.
B. p* < AVC.
C. p* < MC.
D. p* + e < AFC.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is one source of disagreement between economists?
A. Some facts about the economy are unknown. B. Economists differ in their political persuasions. C. Economic theory may not always give an unambiguous answer to a question. D. Solving one problem may make another problem worse. E. All of these responses are correct.
Consider the market for ride-on lawn mowers and the recent increases in the price of oil. The recent increase in the price of oil makes it more expensive to manufacture ride-on lawn mowers. An increase in the price of oil also makes it more expensive to run a ride-on mower. What factors of demand and/or supply are affected by the changing price of oil?
A. Price of related good, expectations of future B. Price of related good, price of input C. Price of input, income D. Price of input, number of buyers
Economic recovery from recession appears to have begun in
Consider the following hypothetical annual growth rates of real GDP:
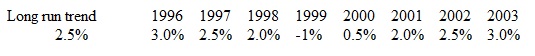
a) 1999
b) 2000
c) 2001
d) 2002
e) 2003
Suppose Russia can produce automobiles relatively cheaply, but they have poor gas mileage and create a great deal of air pollution. The U.S. government, concerned about the quality of air, would like to see fewer Russian automobiles and more cleaner-running American automobiles on the road.a. What is the nature of the market failure that would justify the U.S. government taking some action against the importation of Russian automobiles?b. Explain why imposing a tariff is a second-best policy to employ in this case and what policy choice would be more efficient.
What will be an ideal response?