Explain the difference between economic growth and stability. Can a country experience both at the same time? Why or why not?
What will be an ideal response?
Economic growth refers to an increase in the total output of the economy. Stability occurs when output is steady or growing, with low inflation and full employment of resources. Yes, a country can experience both economic growth and stability at the same time, as long as the increase in output is not accompanied by a rising price level. The late 1990s were a period of growth for the U.S. economy with low inflation.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not a potential drawback to public provision of public goods?
a. Public provision lacks clear signals about the value of the good being produced, possibly leading to under and over provision of the goods. b. Many collective consumption goods might be overproduced private goods. c. Public provision often implies taxation, which creates an excess burden that might overwhelm any efficiency gains. d. Many collective consumption goods are really impure private goods and thus the efficient level of output is never reached.
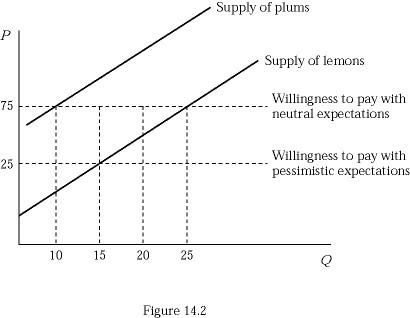 Figure 14.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how much will they pay for a used camera?
Figure 14.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how much will they pay for a used camera?
A. $25 B. $50 C. $75 D. $125
At the equilibrium level of GDP:
A. MV = nominal GDP. B. MV = real GDP. C. M = nominal GDP. D. V = 1/MPS.
To get a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive labor market to hire another worker, the firm will need to
A. raise the wage rate paid to that last worker hired and also to all previous workers hired. B. lower the wage rate paid to that last worker hired and also to all previous workers hired. C. lower the wage rate paid to the last worker hired only. D. raise the wage rate paid to the last worker hired only.