A monochromatic beam of light in air has a wavelength of 632 nm. It passes through glass (n = 1.52) and then through carbon disulfide (n = 1.63). What is its wavelength in the carbon disulfide?
a. 361 nm
c. 895 nm
b. 960 nm
d. 388 nm
D
You might also like to view...
A light beam is shining on a metal target that has a work function of 1.8 eV. If a stopping potential of 0.7 V is required, what is the wavelength of the incoming monochromatic light? (h = 6.63 × 10^?34 J?s, c = 3.00 × 10^8 m/s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10^?19 J, and 1 nm = 10?9 m)
a. 497 nm b. 166 nm c. 796 nm d. 1130 nm e. 691 nm
Why does the very thin region at the top of a soap bubble sometimes appear black?
a. Because no light passes through it. b. Because inverted light waves and non-inverted light waves reflecting from the two surfaces cancel each other. c. Because it is too thin to reflect light. d. Because both reflected waves are inverted or else neither is inverted. e. Because the rest of the film creates a shadow that obscures the colors we would otherwise see.
Coulomb's Law: The figure shows two tiny 5.0-g spheres suspended from very light 1.0-m-long threads. The spheres repel each other after each one is given the same positive charge and hang at rest when ? = 4.1°. What is the charge on each sphere? (k = 1/4??0 = 9.0 × 109 N ? m2/C2) 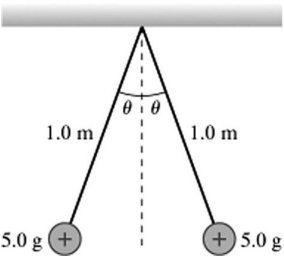
A. 22 nC B. 89 nC C. 360 nC D. 180 nC E. 45 nC
At an altitude of 3 times the radius of the Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is
a. g/3. c. g/27. b. g/9. d. not given.