Which of the following most clearly distinguishes between positive and normative economics?
a. Positive economics is the study of what ought to be; normative economics is concerned with the facts.
b. Positive economics is the study of the facts; normative economics is concerned with what ought to be.
c. Positive economics is the study of supply and demand in narrowly defined markets such as the market for shoes; normative economics focuses on highly aggregated markets such as the market for all consumer products.
d. Positive economics is the study of goods that are scarce; normative economics is concerned with goods that are not scarce.
B
You might also like to view...
If a developing country has sufficient reserves, the buying and selling of foreign currency by the central bank is:
A. likely to have a much smaller impact on the exchange rate than in developed countries. B. completely ineffective on the exchange rate. C. likely to have a much greater impact on the exchange rate than in developed countries. D. likely to have roughly the same impact on the exchange rate as in developed countries.
Command-and-control policies lead to higher prices for consumers than pollution taxes do.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.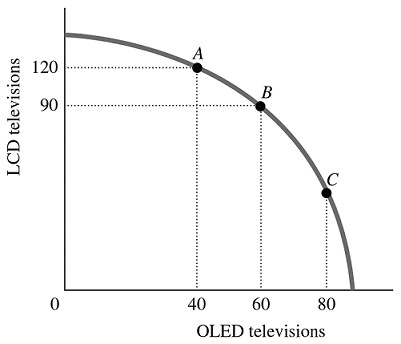 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The best point for society would be
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The best point for society would be
A. either Point B or Point C, as the total amount being produced at either of these points is approximately the same. B. at any of the labeled points, as all of the points represent an efficient allocation of resources. C. Point C, as at this point there are approximately equal amounts of LCD and OLED televisions being produced. D. indeterminate from this information, as we don't have any information about the society's desires.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. When a bank buys government securities from the Fed, then the bank's ability to "create money" will be reduced. 2. A check for $10,000 drawn on Bank A and deposited at Bank B will increase the excess reserves in Bank B by $10,000. 3. The federal funds rate is the interest rate that the Fed charges banks for its loans to them. 4. One bank can borrow reserves from another bank, and the interest on the loan is called the federal funds rate. 5. If a bank has excess reserves of $100,000, then it can lend out only up to $100,000; but if the banking system has excess reserves of $100,000, then the system can make additional loans totaling more than $100,000.