Observers in all reference frames will agree (perhaps by tracking individual electrons) that the bar’s left side becomes negatively charged and its right side becomes positively charged, meaning that just after the bar begins to move (but before the charges have time to pile up at the ends) some leftward electromagnetic force must have been acting on the bar’s electrons. What type of force is this 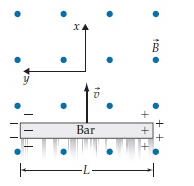 in the implied reference frame of the diagram above?
in the implied reference frame of the diagram above?
A. The force is purely electric.
B. The force is purely magnetic.
C. The force is both electric and magnetic.
D. There is no force on the bar’s electrons in this frame.
B. The force is purely magnetic.
You might also like to view...
perpendicular to the jet’s path from left to right, which part of the airplane becomes negatively charged?
A. Its nose B. Its tail C. Its top D. Its bottom E. Its left wing F. Its right wing T. (No part becomes charged.)
The prefixes which are abbreviated p, n, and T represent which of the following?
a. 10-2, 10-6, and 1015 c. 10-12, 10-9, and 1012 b. 10-9, 106, and 1010 d. 10-15, 10-6, and 1015
A suitcase is sitting on a horizontal conveyor belt, which is moving at speed v. The work done by the frictional force on the suitcase is a. positive
b. negative. c. zero. d. impossible to determine without knowing the mass of the suitcase.
Consider a region of space where the electric field is uniform with magnitude 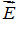 , as shown below. What is the value of the specified potential difference in each case? (a) ?B - ?A? (b) ?C - ?B? (c) ?A - ?C?
, as shown below. What is the value of the specified potential difference in each case? (a) ?B - ?A? (b) ?C - ?B? (c) ?A - ?C?
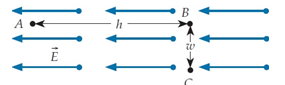
A. 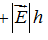
B. 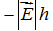
C. 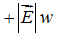
D. 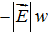
E. 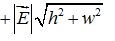
F. 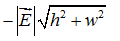
T. zero