Compounds 1 and 2 have the following vapor pressures, in bar, and mixtures of these compounds in the vapor phase are well described as ideal gases at pressures of up to 5 bar.

The liquid molar volumes of these compounds are V1=125 cm3/mol and V2=90 cm3/mol, and can be assumed constant over the range of temperatures and pressures considered in this problem.
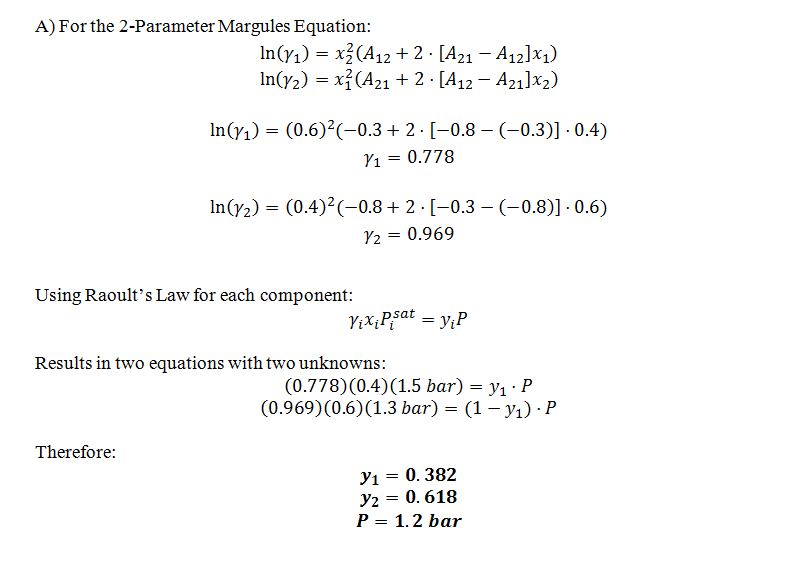
A) Mixtures of 1 and 2 at 80 ?C are well described by the two-parameter Margules equation, with A12 = -0.3 and A21 = -0.8. Compute the pressure and composition of a vapor phase that is in equilibrium with a liquid that contains 40 mol% compound 1 and 60 mol% compound 2 at 80 ?C.
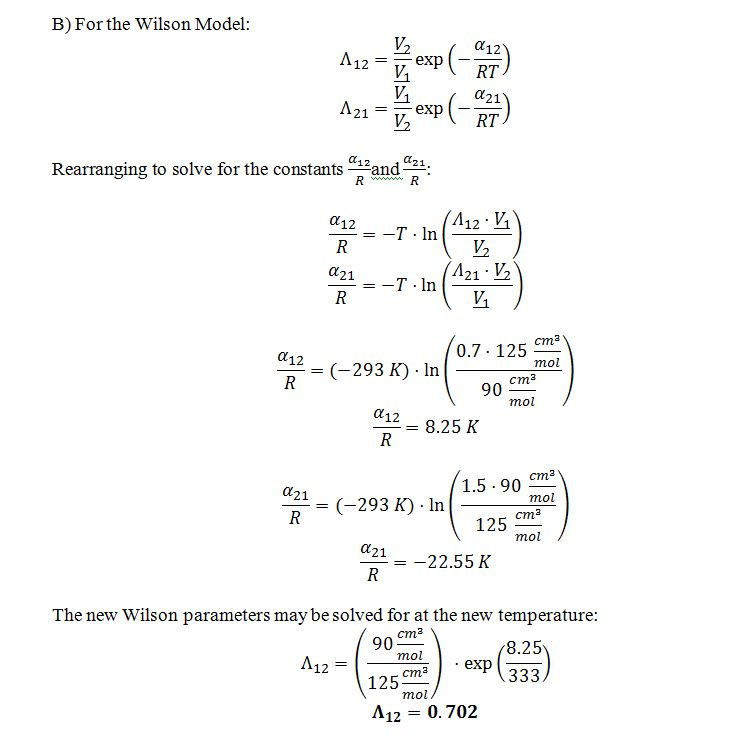
B) The Wilson parameters for this system are ?12=0.7 and ?21=1.5 at 20 ?C. What are ?12 and ?21 at 60 ?C?
C) Using the Wilson parameters given in part B, determine the “infinite dilution” activity coefficients for compounds 1 and 2 at 20 ?C.
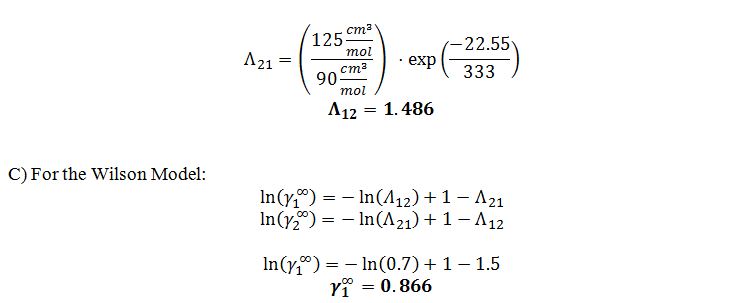
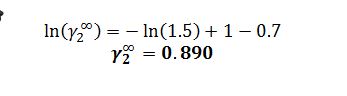
You might also like to view...
For which substance would the particle density equal the bulk density?
A) a soil clod B) a well-aggregated surface soil C) an organic soil D) a quartz pebble E) a wet soil
DOT 3 brake fluid can absorb ________ % of its volume of water per year
A) 15% B) 50% C) 2% D) None of these
A mat of reinforcing bars used in a slab is usually supported above the subgrade at a distance of _____
a. 3 inches b. 4 inches c. 5 inches d. 6 inches
A device that exhibits a change in resistance based on a change in pressure is called a
A) psi gage B) pressure transducer C) gage transducer D) none of the above