Exhibit 20-6 Money, investment and product markets
?
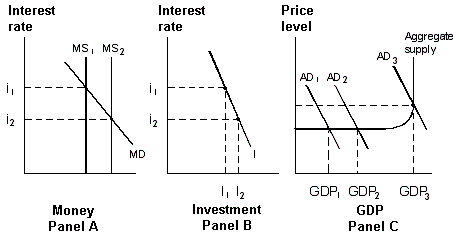
In Exhibit 20-6, an increase in the money supply from MS1 to MS2 causes:
A. interest rates to fall from i1 to i2 and the quantity demanded of investment to decrease from I2 to I1.
B. interest rates to fall from i1 to i2 and aggregate demand to shift from AD2 to AD1.
C. interest rates to fall from i1 to i2 and the quantity demanded of investment to increase from I1 to I2.
D. interest rates to rise from i2 to i1 and the quantity demanded of investment to remain the same.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
All of the following are part of an economic model except
A) data. B) opinions. C) assumptions. D) hypotheses.
The interest rate compensates
a. bankers for their time spent on paperwork b. borrowers for their increased consumption today c. savers for consumption forgone today d. consumers for more consumption today e. the Fed for its efforts to control the money supply
National income: a. is a measure of the income earned by owners of resources used in making final goods and services. b. is a measure of the income received by persons after taxes
c. equals aggregate income minus the statistical discrepancy. d. equals GDP minus depreciation.
Suppose the government sets a price floor that is above the equilibrium price for a given good. It can be said that at the price floor,
A) although sellers are selling all of the product that they desire at this price, the consumers are not able to buy all that they desire. B) although consumers are purchasing all of the product that they desire at this price, the sellers are not selling all that they desire. C) both sellers and buyers are satisfied with the quantity that is being exchanged. D) both sellers and buyers are exchanging the equilibrium quantity of this good. E) b and d