Suppose a presidential candidate promises to increase the government budget surplus and claims that doing so will stop U.S. citizens from investing in foreign companies and increase the value of the dollar. Evaluate this candidate's promise
An increase in the government budget surplus will cause U.S. interest rates to fall. The decline in interest rates will increase domestic investment, but it will also cause Americans to look for higher returns abroad, which means that net capital outflow rises rather than falls as promised. To take advantage of these higher returns, Americans will supply more dollars in the foreign-currency exchange market so the dollar will depreciate rather than appreciate as promised.
You might also like to view...
On a production possibilities frontier diagram, where are production points that have tradeoffs? Where are production points with a free lunch?
What will be an ideal response?
When the price of chai tea lattés is $5, Maxine buys 20 per month. When the price is $4, she buys 30 per month. Maxine's demand for chai tea lattés is
a. elastic, and her demand curve would be relatively flat. b. elastic, and her demand curve would be relatively steep. c. inelastic, and her demand curve would be relatively flat. d. inelastic, and her demand curve would be relatively steep.
A large "T-statistic" tell us that
A) a tiny change in the independent variable will cause a relatively large change in the dependent variable. B) we do not have enough data to obtain an accurate regression line. C) we can be confident that our estimated coefficient is not zero. D) we should have included more "lags" in our model. E) we have incorrectly switched the dependent and independent variables in our model.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.11 below to answer the question(s) that follow.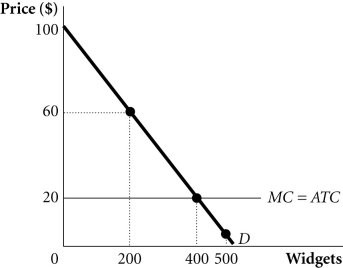 Figure 13.11Refer to Figure 13.11. Suppose a monopolist faces the demand and costs in the figure and is able to perfectly price discriminate. What is the societal loss from having a monopoly instead of a perfectly competitive industry supplying widgets?
Figure 13.11Refer to Figure 13.11. Suppose a monopolist faces the demand and costs in the figure and is able to perfectly price discriminate. What is the societal loss from having a monopoly instead of a perfectly competitive industry supplying widgets?
A. $0 B. $4,000 C. $16,000 D. Indeterminate from the given information.