Briefly describe two key pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory.
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: The two key pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory are the cosmic microwave background and the observed helium content of the universe. The cosmic microwave background consists of photons arriving at Earth directly from the end of the era of nuclei. The radiation came from the heat of the universe and should have a thermal radiation spectrum with a peak wavelength corresponding to 3000 K, the temperature the universe was at the end of that era. Since the universe has expanded by a factor of about 1000 since that time, we observe the radiation with a peak wavelength of about a millimeter, corresponding to a temperature of 2.73K. The Big Bang theory predicts that the universe should have had a composition of 75 percent hydrogen and 25 percent helium by mass at the end of the era of nucleosynthesis. The Milky Way's helium fraction is about 28 percent, and no galaxy has a helium fraction lower than 25 percent.
You might also like to view...
Aluminum has a higher specific heat capacity than iron. This means that for equal masses of aluminum and iron, the metal that heats more quickly when the same amount of heat is applied is
A) aluminum. B) iron. C) need more information
A CD with a diameter of 12.0 cm starts from rest and with a constant angular acceleration of 1.00 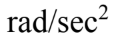 acquires an angular velocity of 5.00 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.00 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the total acceleration of a point 4.00 cm from the center at the time 10.0 seconds from the start?
acquires an angular velocity of 5.00 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.00 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the total acceleration of a point 4.00 cm from the center at the time 10.0 seconds from the start?
A. 0.65 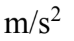
B. 1.00 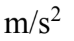
C. 1.25 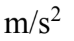
D. 1.37 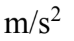
E. 1.86 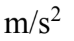
Why can one not use quasars to check the Hubble relation relating distances of objects to their velocity of recession?
What will be an ideal response?
A long cylindrical wire (radius = 2.0 cm) carries a current of 40 A that is uniformly distributed over a cross section of the wire. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point which is 1.5 cm from the axis of the wire?
a. 0.53 mT b. 28 mT c. 0.30 mT d. 40 mT e. 1.9 mT