According to the long-run Phillips curve, in the long run monetary policy influences
a. inflation but not the unemployment rate; this is consistent with classical theory.
b. inflation but not the unemployment rate; this is inconsistent with classical theory.
c. the unemployment rate but not inflation; this is consistent with classical theory.
d. the unemployment rate but not inflation; this is inconsistent with classical theory.
a
You might also like to view...
Goods and services that are used up in the production of other goods and services are called ________ goods and services.
A. final B. nominal C. value added D. intermediate
Withholding of the federal income tax _____
a. was first used during the civil war b. was first used during World War I c. was first used during World War II d. was first used after World War II
Which of the following contains a list only of things that increase when the budget deficit of the U.S. decreases?
a. U.S. supply of loanable funds, U.S. net capital outflow, U.S. domestic investment b. U.S. supply of loanable funds, U.S. exports, the real exchange rate of the dollar c. U.S. interest rates, the real exchange rate of the dollar, U.S. domestic investment d. the real exchange rate of the dollar, U.S. net capital outflow, U.S. net exports
If the economy is at Point A in the Phillips curve graph shown, in the long run, the unemployment would be expected to: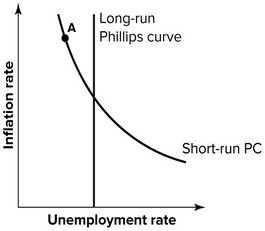
A. decrease. B. immediately fall to zero. C. increase. D. remain constant.