If a union negotiates a wage above the market equilibrium, each firm hiring union members faces
a. a perfectly inelastic supply curve for labor
b. a perfectly elastic supply curve for labor
c. a perfectly inelastic demand curve for labor
d. a perfectly elastic demand curve for labor
e. perfectly inelastic supply and demand curves for labor
B
You might also like to view...
You have a small business that makes $50,000 accounting and economic profit for you. As a disabled person, you must work at home and you did not have other opportunities until your neighbor offers you a job you like equally well for $50,000 and you can do it at home. This means
A. both your accounting and economic profit have gone up. B. your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has stayed the same. C. both your accounting and economic profit have gone down. D. your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has gone up.
Kendra is having difficulty deciding between two cars, A and B. As shown in the accompanying diagram, A has more cargo room than B, but lower gas mileage. Ideally Kendra would like a car both with a lot of cargo room and good gas mileage. 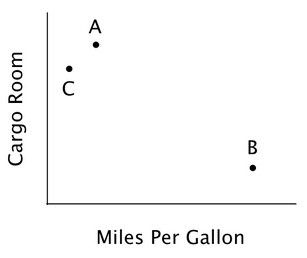 If Kendra behaves like most decision-makers, then the addition of option C would:
If Kendra behaves like most decision-makers, then the addition of option C would:
A. have no impact on her choice of A and B. B. increase her likelihood of picking B. C. increase her likelihood of picking A. D. decrease her likelihood of buying a car.
A phenomenon called Moore's law says:
A. physical capital will double every two years in countries with high rates of growth. B. computing capacity has doubled every two years. C. 70 divided by the growth rate equals how long it will take a country to double its productive capacity. D. 70 divided by the growth rate equals how long it will take a country to double its income level.
A possible solution to the problems of external benefits is
A. to restrict the amount of the good through direct government regulation. B. to tax those receiving the extra benefits. C. production of the good by government. D. effluent fees.