Describe new growth theory. Explain how it differs from neoclassical growth theory
Economists, such as Paul Romer, who adhere to new growth theory, believe that technology is endogenous. This means that technology is part of the economic system and that the amount and quality of technology that is developed varies directly with the amount of resources devoted to it. Neoclassical growth theory advocates emphasized only labor and capital and believed that technology was exogenous. Therefore, they held that technology was outside of our control.
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the following question.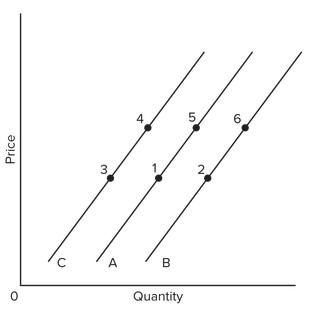 An increase in supply would best be reflected by a change from
An increase in supply would best be reflected by a change from
A. point 2 to point 5. B. point 1 to point 3. C. point 1 to point 2. D. point 3 to point 4.
The above table shows marginal costs and marginal benefits of clean air in a particular industrial area. In the table, when the quantity of clean air is at 25 percent
A) the quantity of polluted air is 25 percent. B) the marginal benefit of clean air exceeds the marginal cost. C) the marginal benefit of clean air is less than the marginal cost. D) the quantity of clean air is optimal.
Which of the following is an example of a final good or service?
a. Bricks purchased by a company for constructing houses b. Wheat purchased by a bakery c. Steel purchased by a company for manufacturing cars d. A cup of coffee bought at a restaurant e. A used car bought by a person
Monopoly as a market structure leads to
a. prices equal to average cost. b. quick response to economic change. c. prices that equal minimum long-run average cost. d. persistent economic profits.