Contractionary fiscal policy to prevent real GDP from rising above potential real GDP would cause the inflation rate to be ________ and real GDP to be ________
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
To achieve long-run equilibrium in an economy with a recessionary gap, without the use of stabilization policy, the inflation rate must:
A. not change. B. increase. C. decrease. D. either increase or decrease depending on the relative shifts of AD and AS.
When economic growth (a gradual shift of LRAS to the right) expands the production possibilities of an economy,
a. a higher rate of real output can be achieved in the short run, but it cannot be sustained in the long run. b. a larger output can be attained even if unemployment remains at its natural rate. c. the general level of prices will rise if the money supply is held constant. d. the equilibrium in the goods and services market will be disrupted.
The costs of recruiting new employees, training the new employees, and suffering the initial low productivity of new employees when old employees leave are called
A. benchmark wages. B. efficiency wages. C. turnover costs. D. marginal costs of long-term training.
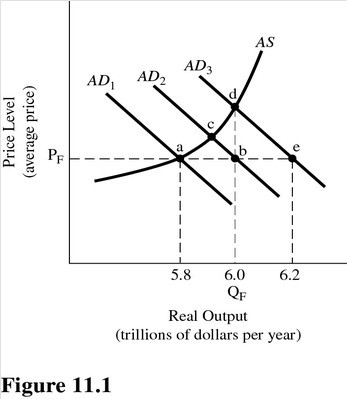 In Figure 11.1, assume that QF is full-employment output and the level of aggregate spending is represented by AD1. If AD1 increases to AD2, which of the following statements is correct?
In Figure 11.1, assume that QF is full-employment output and the level of aggregate spending is represented by AD1. If AD1 increases to AD2, which of the following statements is correct?
A. Excess AD and inflation will be the result. B. Full employment will not be reached because some of the additional spending results in higher prices rather than higher output. C. A lower price level will result. D. Full employment will be reached.