Which of the following cushions and protects
internal organs yet moves independently of the
body wall?
a. the coelom
b. the mesoderm
c. the protostome
d. the gastrovascular cavity
e. the endoderm
A
You might also like to view...
A child swinging on a swing utilizes which type (or types) of energy?
a. kinetic energy only because the child is in constant motion b. potential energy only, because the child has to invest energy to get the swing to go c. chemical energy only, because it is the child's metabolism that powers the muscles that make the swing move d. kinetic and potential energy only, but in constantly changing ratios: when changing direction it is pure potential energy; at the bottom of the arc, it is pure kinetic energy e. kinetic, potential, and chemical energy. The child powers the swing with chemical energy in the muscle cells and the swing moves like a pendulum with changing ratios of kinetic and potential energy.
Alternate forms of the same gene
A. do not exist. B. are alleles. C. do not occur in the same individual. D. are homologs. E. are sister chromatids.
Contraction of the fibers labeled A in Figure 40-2 results in:
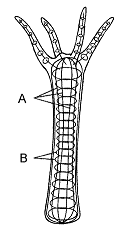
a. elongation of the body.
b. elongation of the tentacles.
c. elongation of the gastrovascular cavity.
d. shortening of the body.
e. expansion of the pedal disk.
The oxygen required by cellular respiration is reduced and becomes part of which molecule?
a. ATP b. H2O c. pyruvate d. CO2