When the price of a good is legally set below the equilibrium level, a shortage often results. This shortage
a. is a temporary failure of the market mechanism.
b. is the result of a shift in demand.
c. is the result of a shift in supply.
d. occurs because the price ceiling prevents the market mechanism from establishing an equilibrium price.
D
You might also like to view...
If a perfectly competitive wheat farmer is maximizing its profit and then increases its output, the farmer's
A) total revenue increases, but total cost rises by more so that the farmer's total profit decreases. B) total revenue decreases and total cost increases, both thereby decreasing the farmer's total profit. C) total revenue does not change but total cost increases, thereby decreasing the farmer's total profit. D) marginal revenue increases, but so does marginal cost, so that the farmer's total profit increases. E) total revenue and total cost both rise, but the effect on the farmer's total profit is uncertain.
Another commonly used algebraic form for a demand function is the semi-logarithmic functional form, log(Q) = a - bP + cI, where Q is quantity demanded, P is the product price, and I is income
Here, -100b represents the percentage change in quantity demanded given a one unit increase in price. By the Law of Demand, we should expect the value of b to be: A) positive. B) negative. C) positive or negative. D) We do not have enough information to answer this question.
The natural rate of unemployment is that rate at which the economy achieves its potential real GDP
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
If you wanted to produce at an output of 80, in the long run you would choose a plant whose size is represented by
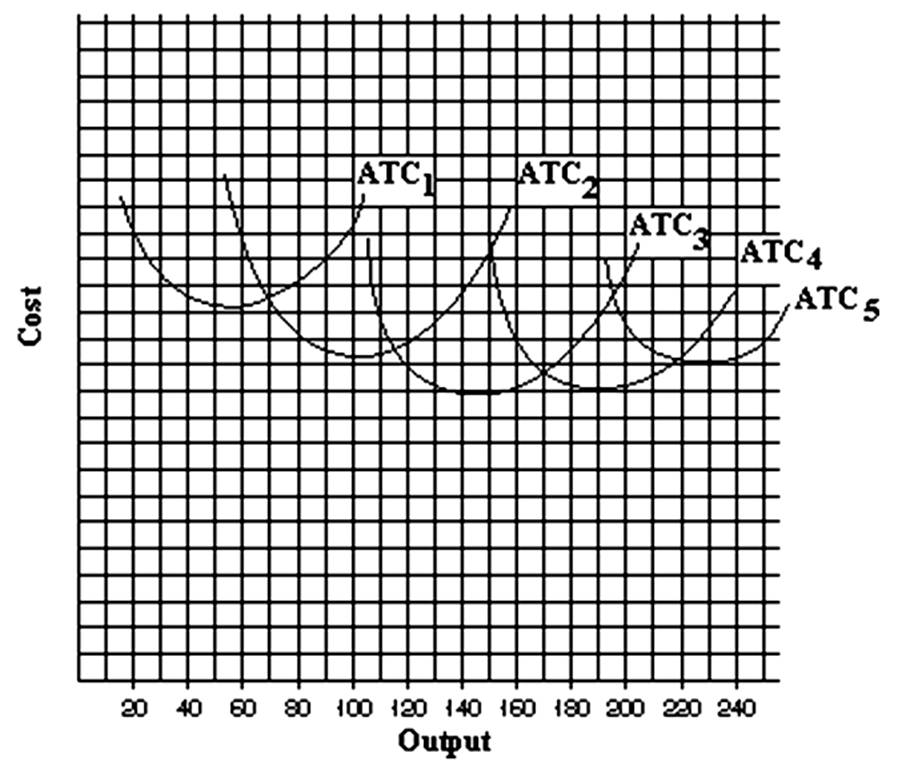
A. ATC1.
B. ATC2.
C. ATC3.
D. ATC4.