How does the idea of independent events help in explaining the gambler's fallacy in a roulette game?
What will be an ideal response?
The gambler's fallacy refers to the assumption that random outcomes tend to avoid repeats. In a roulette game, outcomes are random and independent. Two random outcomes are said to be independent when knowing about one outcome does not help predict the other outcome. Hence, the outcome of one roulette game has nothing to do with the outcome of the next game and the idea that outcomes of a roulette game tend to avoid repeats is a fallacy.
You might also like to view...
In the classical model, a tax on capital will
a. increase the demand for labor, the real wage, and output. b. increase the supply of labor, reduce real wages, and increase output. c. decrease the demand for labor, the real wage, and output. d. have no effect on the labor market. e. increase both labor demand and supply, which will increase output.
According to the graph shown, the change in consumer surplus brought about by the imposition of a tariff to an economy previously open to free trade is:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
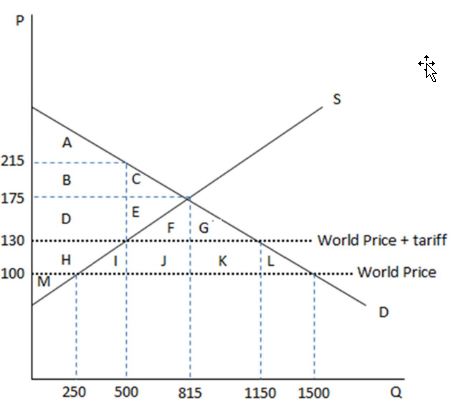
A. an increase of HIJKL.
B. a loss of HIJKL.
C. a gain of DE.
D. a loss of DE.
Unconventional monetary policy tools include all but:
A. forward guidance. B. reserve requirement. C. targeted asset purchases. D. quantitative easing.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 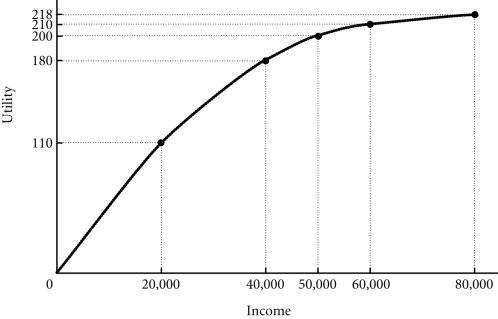 Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. Suppose John's utility from income is given in the figure. From this we would say that John is
Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. Suppose John's utility from income is given in the figure. From this we would say that John is
A. risk-loving. B. risk-averse. C. a risk taker. D. risk-neutral.