Using the figure above, identify the labeled part.
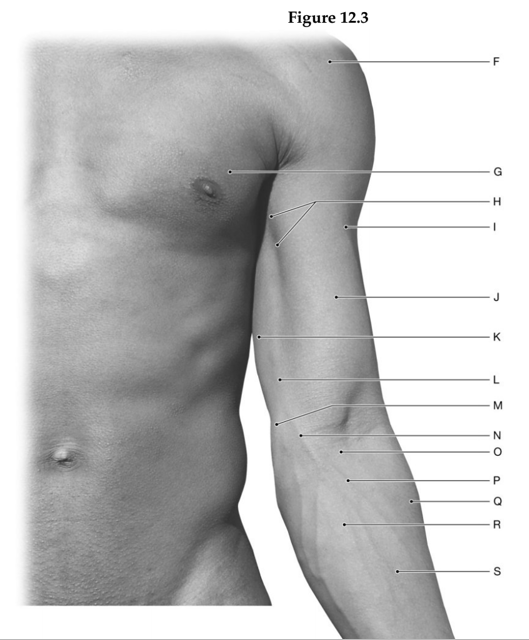
1. Label A: ______________________________
2. Label B: ______________________________
3. Label C: ______________________________
4. Label D: ______________________________
5. Label E: ______________________________
6. Label F: ______________________________
7. Label G: ______________________________
8. Label H: ______________________________
9. Label I: ______________________________
10. Label J: ______________________________
11. Label K: ______________________________
12. Label L: ______________________________
13. Label M: ______________________________
14. Label N: ______________________________
15. Label O: ______________________________
16. Label P: ______________________________
17. Label Q: ______________________________
18. Label R: ______________________________
19. Label S: ______________________________
20. Label T: ______________________________
21. Label U: ______________________________
1. Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
2. Tendon of palmaris longus muscle
3. Tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
4. Head of ulna
5. Pisiform bone with palmaris brevis muscle
6. Deltoid muscle
7. Pectoralis major muscle
8. Coracobrachialis muscle
9. Cephalic vein
10. Biceps brachii muscle
11. Triceps brachii muscle, long muscle
12. Basilic vein
13. Medial epicondyle of humerus
14. Median cubital vein
15. Cubital fossa
16. Median antebrachial vein
17. Brachioradialis muscle
18. Pronator teres muscle
19. Flexor carpi radialis muscle
20. Tendon of flexor carpi radialis muscle
21. Site for palpation of radial pulse
You might also like to view...
One cause for insulin resistance in non-insulin dependent (Type II) diabetes is
A) insulin receptor up-regulation. B) decreased insulin secretion. C) decreased cortisol secretion. D) insulin receptor down-regulation. E) cortisol receptor up-regulation.
Proteins must first be enzymatically degraded to single amino acids before entering the capillaries of the hepatic portal system. Is this true or false? What is the significance of this? Is absorption of carbohydrates and lipids restricted to monomers? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
When sitting upright, you are resting on your
a. pubic bones. b. ischial tuberosities. c. sacroiliac joints. d. iliac crest.
The term "tonicity" refers to
A. the secretion of products outside of the cell through the plasma membrane. B. the effects of filtration on a cell. C. the effect of a solution on water movement into or out of cells. D. the separation of one cell into two daughter cells.