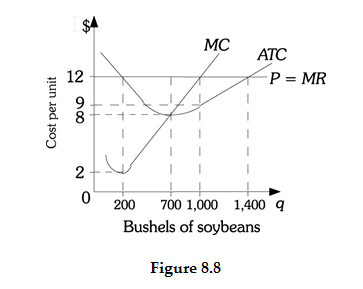
Refer to Figure 8.8. If this farmer is producing the profit-maximizing level of output, her profit is
A) $0.
B) $2,800.
C) $3,000.
D) $12,000.
C) $3,000.
You might also like to view...
Assume that the central bank purchases government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and current international transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. b. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and current international transactions become more positive (or less positive). c. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and current international transactions remain the same. d. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and current international transactions become more positive (or less negative). e. The real risk-free interest rate and current international transactions remain the same.
Waldo works eight hours and produces 7 units of goods per hour. Emerson works six hours and produces 10 units of goods per hour
a. Waldo's productivity and output are greater than Emerson's. b. Waldo's productivity is greater than Emerson's but his output is less. c. Emerson's productivity and output are greater than Waldo's. d. Emerson's productivity is greater than Waldo's but his output is less.
Frank is considering moving to Denver. There is a 70 percent chance that he will find a job that pays $1,000 more than what he currently earns and a 30 percent chance he will find one that pays $3,000 less. The expected value of moving to Denver is:
A. $200. B. -$200. C. $700. D. $900.
At the profit-maximizing level of output, a monopolist will always operate where:
A. average total cost equals marginal cost. B. price is greater than average revenue. C. price is greater than marginal cost. D. total revenue is greater than total cost.