Refer to the information provided in Figure 25.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.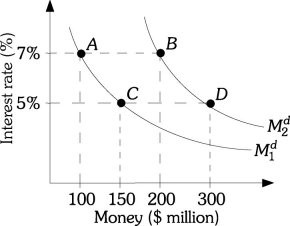 Figure 25.2Refer to Figure 25.2. Suppose that money demand is currently at Point B. A movement to Point D could be caused by
Figure 25.2Refer to Figure 25.2. Suppose that money demand is currently at Point B. A movement to Point D could be caused by
A. an increase in the price level, ceteris paribus.
B. an increase in nominal income, ceteris paribus.
C. a decrease in the price level, ceteris paribus.
D. a decrease in the interest rate, ceteris paribus.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The marginal cost curve intersects the minimum point of the average variable cost curve
a. True b. False
A profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm must decide:
A. only which industry to join, taking price and output as fixed. B. only how much to produce, taking price as fixed. C. only what price to charge, taking output as fixed. D. both what price to charge and how much to produce.
The demand for cars in a certain country is given by: D = 20,000 - P, where P is the price of a car. Supply by domestic car producers is: S = 5,000 + 0.5. If this economy is open to trade, and the world price of a car is $6,000, and the government imposes a quota allowing 3,000 cars to be imported, then domestic price of the car will be ________.
A. $8,000 B. $6,000 C. $5,000 D. $10,000
Total planned expenditures in a closed economy are equal to
A. investment + saving + transfers. B. consumption + savings + transfers + investment. C. consumption + investment + government expenditures. D. saving + investment + government expenditures.