If a consumer is choosing the bundle of goods that maximizes utility subject to a budget constraint, then
A. the rate at which income affects the utility-maximizing choice is equal for all goods.
B. the ratio of marginal utility to price is equal for all goods.
C. the rate at which the consumer is willing to substitute between goods is equal to the market rate of exchange.
D. both b and c
E. all of the above
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Suppose two companies, Macrosoft and Apricot, and considering whether to develop a new product, a touch-screen t-shirt. The payoffs to each of developing a touch-screen t-shirt depend upon the actions of the other, as shown in the payoff matrix below (the payoffs are given in millions of dollars). 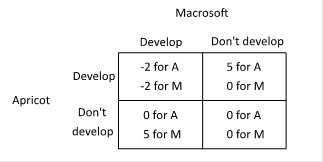 Suppose Apricot makes its decision first, and then Macrosoft makes its decision after seeing Apricot's choice. What will happen if, before Apricot chooses, Macrosoft announces that it is going to develop a touch-screen t-shirt no matter what Apricot does?
Suppose Apricot makes its decision first, and then Macrosoft makes its decision after seeing Apricot's choice. What will happen if, before Apricot chooses, Macrosoft announces that it is going to develop a touch-screen t-shirt no matter what Apricot does?
A. Neither Apricot nor Macrosoft will develop a touch-screen t-shirt because they will both realize that they are in a no-win situation. B. Apricot will develop a touch-screen t-shirt, and Macrosoft will not because Macrosoft's threat is not credible. C. Macrosoft will develop a touch-screen t-shirt, and Apricot will not because it's not in Apricot's interest to develop a touch-screen t-shirt if Macrosoft also develops one. D. Both Apricot and Macrosoft will develop a touch-screen t-shirt because neither company will want to back down.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the United States led to _____
a. the introduction of the concept of discrimination. b. complete elimination of discrimination from the labor force. c. the creation of equal opportunities for men and women. d. the creation of equal opportunities for the members of different races. e. the establishment of a much clearer definition of discrimination.
Employers and workers in the protected industry know that the consequences of protection are principally:
a. lower prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. b. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. c. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. d. lower prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. e. higher prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers.
In which of the following periods did nations of the European Union experience the lowest average annual rate of growth of per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
A. 1981-1990 B. 1991-2000 C. 2001-2010 D. 2011-2017