What is disposable income? How is it calculated?
Disposable income (DI) is the sum of the incomes of all individuals in the economy after all taxes have been deducted and all transfer payments have been added.
DI = GDP ? Taxes + Transfer payments
= GDP ? (Taxes ? Transfers)
= Y ? T
where Y represents GDP and T represents taxes net of transfers or simply net taxes.
You might also like to view...
Suppose that the bank has the following balance sheet:
Assets Liabilities Reserves $75,000 Deposits $500,000 Loans $430,000 Net worth $5,000 If the required reserve ratio is 10 percent, what is the maximum the bank can loan out? Suppose the bank makes this loan and the borrower spends the money, which is deposited in a different bank. Show the impact of these transactions on the bank's balance sheet.
Demand-side inflation differs from supply-side inflation in the following way:
a. demand-side inflation has higher output; supply-side inflation has lower output. b. demand-side inflation has lower output; supply-side inflation has higher output. c. demand-side inflation is always followed by stagflation; supply-side inflation is always followed by demand-side inflation. d. demand-side inflation has a self-correcting mechanism; supply-side inflation does not.
The goal of rent control is to help the poor by making housing more affordable
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the following graph to answer the question: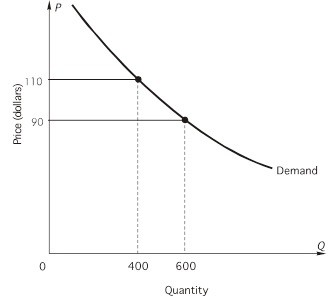 Suppose price rises from $90 to $110. Using representative arrows, the price effect is a relatively ________ (short, long) arrow pointing ________ (upward, downward).
Suppose price rises from $90 to $110. Using representative arrows, the price effect is a relatively ________ (short, long) arrow pointing ________ (upward, downward).
A. long; downward B. short; upward C. short; downward D. long; upward