The grade distribution in this class will fit a bell curve as shown below. 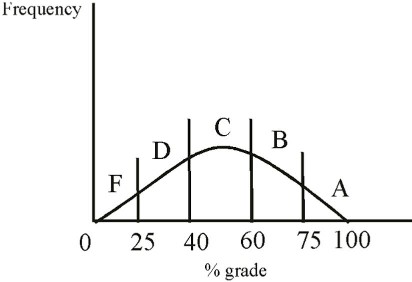 You have no knowledge of what your ability level is relative to the other students and you have no idea how hard the test will be for you. You could fall anywhere on the distribution as far as you know at this time. Now your professor makes you an offer. You have the opportunity to alter the grading brackets to make them anything you want. The only constraint is that the overall class GPA must not change from the 2.0 that is the present distribution. Sketch on the graph below your optimal distribution given these constraints and explain why you made any changes.
You have no knowledge of what your ability level is relative to the other students and you have no idea how hard the test will be for you. You could fall anywhere on the distribution as far as you know at this time. Now your professor makes you an offer. You have the opportunity to alter the grading brackets to make them anything you want. The only constraint is that the overall class GPA must not change from the 2.0 that is the present distribution. Sketch on the graph below your optimal distribution given these constraints and explain why you made any changes.
src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__rrrr0821190959__f1q42g2.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="253" width="427" />
What will be an ideal response?
Most students sketch a much higher distribution with the A's and the F's eliminated. They are willing to trade away the possibility of an A for the guarantee that they will not get an F. In other words, they are risk averse. Some students will promote all C's in the distribution.
Economics
src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__rrrr0821190959__f1q42g2.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="253" width="427" />
What will be an ideal response?
Most students sketch a much higher distribution with the A's and the F's eliminated. They are willing to trade away the possibility of an A for the guarantee that they will not get an F. In other words, they are risk averse. Some students will promote all C's in the distribution.

You might also like to view...
For an economy starting at full employment real GDP, a decrease in investment results in a(n)
A. decrease in full-employment output. B. inflationary output gap. C. recessionary output gap. D. increase in full-employment output.
A business produces 4,000 units per month which it sells at $20/unit. Costs include: $10,000 on raw materials, $15,000 in wages for operators and $10,000 in wages to sales people. If the business is just breaking even, what are its fixed costs:
a. $35,000 b. $40,000 c. $45,000 d. $50,000
The basic incentive problem associated with internal transfers is that:
A. divisional managers have only public information about opportunity costs. B. divisional managers have private information about opportunity costs. C. senior management make all information about opportunity costs public. D. senior management have private information about opportunity costs.
Variations in the standard of living across countries is due almost entirely to differences in each nation's total output of goods and services
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false