Refer to the diagram. Points A, B, C, D, and E show:
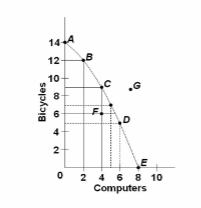
A. that the opportunity cost of bicycles increases, while that of computers is constant.
B. combinations of bicycles and computers that society can produce by using its resources
efficiently.
C. that the opportunity cost of computers increases, while that of bicycles is constant.
D. that society's demand for computers is greater than its demand for bicycles.
B. combinations of bicycles and computers that society can produce by using its resources
efficiently
You might also like to view...
An increase in nominal gross domestic product necessarily entails an increase in
A) both real output and the price level. B) either real output or the price level (or both). C) real output and employment. D) the price level and employment.
For identical cost conditions, the long-run equilibrium price under any form of imperfect competition is ____ than the long-run equilibrium price in perfect competition because of ____.
a. higher; perfectly elastic demand in imperfect competition. b. higher; less than perfectly elastic demand in imperfect competition. c. lower; perfectly elastic demand in imperfect competition. d. lower; less than perfectly elastic demand in imperfect competition.
If there is complete crowding out, the change in Real GDP that results from a given change in autonomous spending will be
A) zero. B) greater than if there was incomplete crowding out. C) infinite. D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
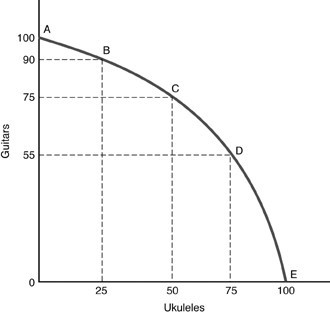 In the above figure, the production of 25 guitars and 25 ukuleles is
In the above figure, the production of 25 guitars and 25 ukuleles is
A. efficient production. B. impossible production. C. inefficient production. D. not possible since production always occurs along the PPC.