Refer to the Laffer Curve above. An increase in the tax rate from T3 to T4 would:
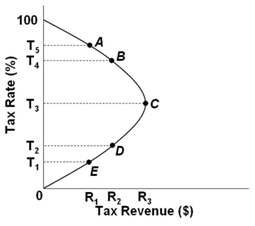
A. Decrease tax revenues and support the views of supply-side economists
B. Increase tax revenues and support the views of supply-side economists
C. Increase tax revenues and support the views of mainstream economists
D. Decrease tax revenues and support the views of mainstream economists
A. Decrease tax revenues and support the views of supply-side economists
You might also like to view...
Bubba's Hula Shack bar and bistro has begun giving customers who can show proof that they arrived at the establishment by public transportation a 10 percent discount on their total bill. This is an example of
A) two-part tariff pricing. B) odd pricing. C) arbitrage. D) price discrimination.
An automatic increase in a wage rate found in some contracts is known as a
A) change of labor agreement. B) cost of labor arrangement. C) cost of living adjustment. D) charge for living amendment.
The bowed-out-from-the-origin shape of the production possibilities curve occurs because resources are
a. equally well-suited to production of both goods b. not being used efficiently c. not always of equal quality and some are better suited to the production of one type of good than others d. increasing as more of one good is produced e. of an increasingly inferior quality
When the percentage change in quantity demanded is numerically less than the percentage change in price, ceteris paribus, demand is:
a) Inelastic. b) Elastic. c) Perfectly elastic. d) Unitary elastic.