In situations where people make decisions with perfectly predictable consequences, traditional economic models cannot explain:
A. why people experience regret.
B. what the rational choice should be.
C. how people maximize their utility.
D. how risk aversion influences decisions.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When more labor is unemployed than the amount at the natural unemployment rate, then real GDP ________ potential GDP
A) is equal to B) is less than C) is greater than D) cannot be compared to
Compare and contrast the relative price elasticities of Marlboro brand cigarettes with cigarettes in general. Why is there a difference?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following examples is elastic but not perfectly elastic?
a. When milk is discounted by 10 percent, sales increase by 20 percent. b. When corn is discounted by 2 percent, sales increase by 100 percent. c. When HD televisions are discounted by 3 percent, sales increase by 200 percent. d. When motorcycles are discounted by 5 percent, sales increase by 500 percent.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 8.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 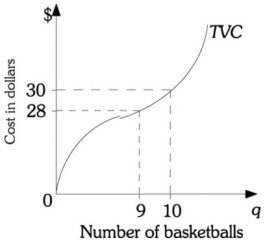 Figure 8.3
Refer to Figure 8.3. The marginal cost of the eleventh basketball is
Figure 8.3
Refer to Figure 8.3. The marginal cost of the eleventh basketball is
A. less than $1. B. $1. C. $2. D. greater than $2.