Length Contraction: A really high-speed train moves in a direction parallel to its length with a speed that approaches the speed of light. The height of the train, as measured by a stationary observer on the ground,
A. approaches infinity.
B. approaches zero.
C. increases slightly.
D. decreases slightly.
E. does not change due to the motion.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
How does the lava that forms a steep-sided volcano (a stratovolcano) compare to the lava that forms a shallow-sloped volcano (a shield volcano)?
A) The lava is thicker (higher viscosity) for the steep-sided stratovolcano. B) The lava is runnier (lower viscosity) for the steep-sided stratovolcano. C) The lava comes from deeper in Earth's mantle for the steep-sided stratovolcano. D) The lava comes from a very shallow layer of Earth's crust for the steep-sided stratovolcano. E) The lava contains more metal for the steep-sided stratovolcano.
What power lens is needed to correct for nearsightedness where the uncorrected far point is 75 cm?
A) -1.33 D B) +1.33 D C) -0.75 D D) +0.75 D E) -1.00 D
By substituting for Eb? (T) performing the integration over the entire spectrum, derive a relationship between ? and the constants C1 and C2
GIVEN
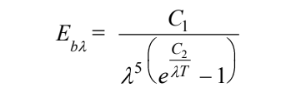
where

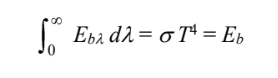
FIND
• A relationship between ? and C1 and C2
The graph above shows 4 models for how the average distance between galaxies could change with time, from the past (left) to now (middle) to the future (right-hand side). The graph also shows real data, based on white dwarf supernovae. Which model(s) predict(s) that galaxies will eventually get closer together?
A) accelerating B) coasting C) critical D) recollapsing E) all of them