A country possesses a comparative advantage in the production of a product if
A) the opportunity cost, in terms of the amount of other products that it gives up to produce this product, is lower than it is for its trading partners.
B) it possesses an absolute advantage in the production of this good compared to its trading partners.
C) it is able to produce less of this good per worker than its trading partners.
D) it can produce more of this good per hour than its trading partners.
A
You might also like to view...
Beginning in the early 1970s, many nations abandoned their dollar standard and moved toward a system of:
A) fixed exchange rates based on gold. B) fixed exchange rates based on the Deutsche Mark. C) floating exchange rates. D) real money systems in which currencies were backed by government bonds.
In the data, we observe that countries with high inflation rates tend to have high nominal interest rates. What does this imply, if anything, about real interest rates in countries with very high inflation rates?
What will be an ideal response?
A higher price level __________ the real value of purchasing power of the publics accumulated savings and balances
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the graph below. Which of the following statements is correct on the basis of the information shown?
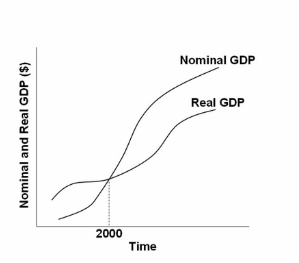
A.
Real GDP must be deflated in each year after 2000 to determine nominal GDP
B.
Nominal GDP must be inflated in each year since 2000 to determine real GDP
C.
Nominal GDP must be deflated in each year before 2000 to determine real GDP
D.
Nominal GDP must be inflated in each year before 2000 to determine real GDP