Marginal cost is equal to ________ when ________ is minimized.
A. average total cost; average variable cost
B. average variable cost; average fixed cost
C. average variable cost; average variable cost
D. average fixed cost; average fixed cost
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following industrial countries experienced a relatively slower growth of real GDP in the latter half of the 1990s?
a. Canada b. United States c. Italy d. France e. Japan
A straight—line production possibilities curve has
A) an increasing opportunity cost between the two goods. B) a decreasing opportunity cost between the two goods. C) a constant opportunity cost between the two goods. D) no opportunity cost between the two goods.
Figure 36-2
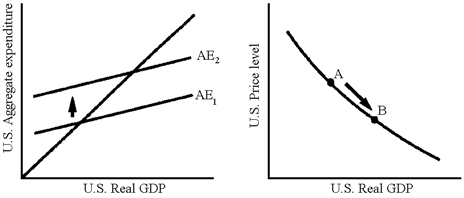
A. An increase in the U.S. price level B. A decrease in the U.S. price level C. An appreciation of the U.S. dollar D. An expansionary monetary policy
Which of the following explains why fluctuations in real GDP have become less volatile in the United States since 1950?
A) Services have become a smaller fraction of GDP since the 1950s. B) Unemployment insurance and other government transfer programs are more prevalent since the 1950s. C) The government has become more reluctant to intervene when real GDP declines and unemployment rises since the 1950s. D) both B and C