With increasing emphasis on energy conservation, the heat loss from buildings has become a major concern. For a small tract house the typical exterior surface areas and R-factors (area ? thermal resistance) are listed below

(a) Calculate the rate of heat loss from the house when the interior temperature is 22°C
and the exterior is –5°C.
(b) Suggest ways and means to reduce the heat loss and show quantitatively the effect
of doubling the wall insulation and the substituting double glazed windows (thermal
resistance = 0.2 m2 K/W) for the single glazed type in the table above.
GIVEN
• Small house
• Areas and thermal resistances shown in the table above
• Interior temperature = 22°C
• Exterior temperature = –5°C
FIND
(a) Heat loss from the house (qa) (b) Heat loss from the house with doubled wall insulation and double glazed windows (qb). Suggest
improvements.
ASSUMPTIONS
• All heat transfer can be treated as one dimensional
• Steady state has been reached
• The temperatures given are wall surface temperatures
• Infiltration is negligible
• The exterior temperature of the floor is the same as the rest of the house
(a) The rate of heat transfer through each element of the house is given
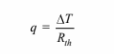
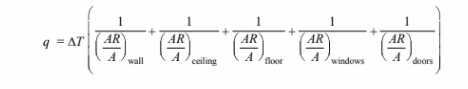
The total rate of heat loss from the house is simply the sum of the loss through each element
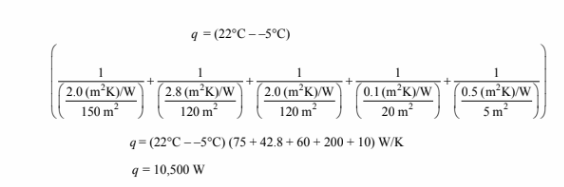
(b) Doubling the resistance of the walls and windows and recalculating the total heat loss
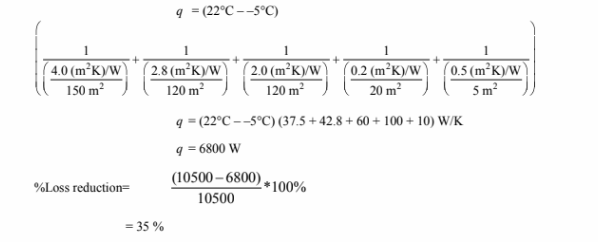
Doubling the wall and window insulation led to a 35% reduction in the total rate of heat loss.
You might also like to view...
What was the first geological period in Earth's history after the dinosaurs became extinct?
A) The Cretaceous Period B) The Carboniferous Period C) The Tertiary Period D) The Triassic Period
Most of our detailed knowledge of the jovian planets comes from the Hubble Space Telescope
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Your largest personal contribution to global warming in a year comes from ________
a. use of freon propellants b. use of air conditioners in your home c. driving your car d. cutting down trees e. burning natural gas for home heating.
What is the escape speed from a planet of mass m and radius r if m = 3.2 × 10^23 kg and r = 2.4 × 10^6 m?
a. 5.5 km/s b. 4.2 km/s c. 5.2 km/s d. 4.8 km/s e. 3.7 km/s