For a given decrease in supply, the condition of demand that will result in no change in quantity is when demand is
A. perfectly inelastic.
B. elastic.
C. perfectly elastic.
D. inelastic.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Figure 10-10
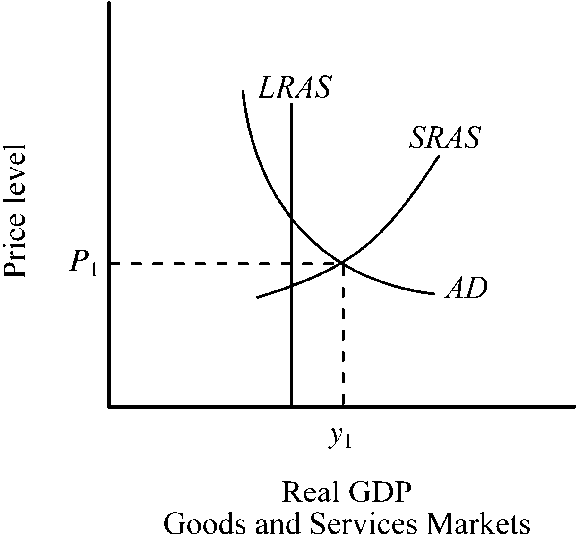
Given the aggregate demand and aggregate supply conditions depicted in , which of the following will tend to occur?
a.
an increase in resource prices, which will shift SRAS to the left
b.
a decrease in resource prices, which will shift SRAS to the left
c.
an increase in the real rate of interest, which will shift aggregate demand to the left
d.
a decrease in the real rate of interest, which will shift aggregate demand to the left
e.
Both b and c are correct.
An increase in the demand for bonds generates
A) an increase in both the interest rate and the exchange rate. B) a decrease in both the interest rate and the exchange rate. C) an increase in the interest rate and a decrease in the exchange rate. D) a decrease in the interest rate and an increase in the exchange rate.
Which of the following examples shows the most inelastic demand?
a. When the price of printers increases from $800 to $1,000 per printer, sales decreases by 20 percent. b. When the price of fedoras increases from $90 to $100 per hat, sales decreases by half. c. When the price of shoes decreases from $60 to $50 per pair, sales increases 5 percent. d. When the price of crackers decreases from $3 to $2 per box, sales double.
The longest economic expansion in the United States occurred during the
A. 1940s. B. 1960s. C. 1990s. D. 1980s.