A ball thrown upwards reaches a maximum height and then comes back down to the original level. At the maximum height
a. the velocity and acceleration both point up.
b. the velocity points up and the acceleration down.
c. the velocity points down and the acceleration up.
d. the velocity and acceleration both point down.
e. the velocity is zero.
f. the acceleration is zero.
e
You might also like to view...
A construction worker pulls a box of tools on a smooth horizontal floor with a force of 100 N in a direction of 37.0° above the horizontal. The mass of the box and the tools is 40.0 kg
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for the box. (b) Calculate the acceleration of the box. (c) How hard does the floor push up on the box? What will be an ideal response?
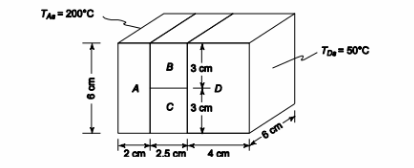
A section of a composite wall with the dimensions shown below has uniform temperatures of 200°C and 50°C over the left and right surfaces, respectively. If the thermal conductivities of the wall materials are: kA = 70 W/(m K), kB = 60 W/(m K), kc = 40 W/(m K) and kD = 20 W/(m K), determine the rate of heat transfer through this section of the wall and the temperatures at the interfaces. including a contact resistance of 0.1 K/W at each of the interfaces.
GIVEN
• Composite wall
• Thermal conductivities:
? kA = 70 W/(m K)
? kB = 60 W/(m K)
? kC = 40 W/(m K)
? kD = 20 W/(m K)
• Surface temperatures
? Left side (TAs) = 200°C
? Right side (TDs) = 50°C
• Contact resistance at each interface (Ri) = 0.1 K/W FIND
(a) Rate of heat transfer through the wall (q) (b) Temperatures at the interfaces
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional conduction
• The system is in steady state
SKETCH
If gravity between the Sun and Earth suddenly vanished, Earth would continue moving in
A) a curved path. B) an outward spiral path. C) an inward spiral path. D) a straight-line path.
A stone is held at a height h above the ground. A second stone with four times the mass of the first one is held at the same height
The gravitational potential energy of the second stone-Earth system compared to that of the first stone-Earth system is A) one-fourth as much. B) one-half as much. C) twice as much. D) four times as much. E) the same.