Recency bias refers to a psychological bias whereby people believe that recent past trends and patterns will continue in the future
How would recency bias explain why investors chase returns? Does return-chasing lead investors to realize a higher rate of return on investments?
Return-chasing involves investing in assets that have realized a high rate of return in the past. Recency bias could explain return-chasing. Recency bias leads people to mistakenly believe that recent past trends and patterns will continue into the future, leading people to chase recent historical returns. As discussed in the Evidence-Based Economics feature in the chapter, research has shown that return-chasing does not usually benefit investors. At 154 of the largest U.S. corporations, employees did not benefit from return chasing.
A-head: EVIDENCE-BASED ECONOMICS: DO INVESTORS CHASE HISTORICAL RETURNS?
Concept: Return chasing
You might also like to view...
The accompanying supply-demand diagram shows the market for calculators. The initial price of calculators is P0, and the initial quantity exchanged is Q0.
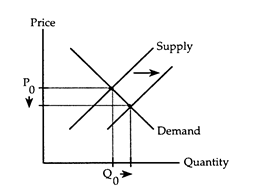
Which of the following situations could be correctly illustrated by the diagram?
a. Graphing capabilities and other new features lead people to buy more calculators.
b. The cost of memory chips used in calculators falls, lowering the price of calculators.
c. Personal computerized notepads with substantial computing power are introduced, reducing people's need for calculators.
d. A heavy tariff is placed on calculators imported from overseas.
In the figure below, label the axes and then draw a demand for money curve. Illustrate an increase in the demand for money
What will be an ideal response?
Nominal values are values measured in terms of the prices at which goods and services are actually sold
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income, all other things being constant, is
A) income elasticity of demand. B) price income elasticity of demand. C) price elasticity of demand. D) cross price elasticity of demand.