A concrete wall with a surface area of 20?m2 and a thickness of 0.30 m separates conditioned room air from ambient air. The temperature of the inner surface of the wall (T1) is maintained at 25°C. (a) Determine the heat loss through the concrete wall for three thermal conductivity values of 0.75, 1, and 1.25?W/m•K and outer wall surface temperatures of T2?=???15, ??10, ??5, 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 38°C (a total of 11 data points for each thermal conductivity value). Tabulate the results for all three cases in one table. Also provide a computer-generated graph [Heat loss, vs. Outside wall temperature, T2(°C)] for the display of your results. The results for all three cases should be plotted on the same graph. (b) Discuss your results for the three cases.
What will be an ideal response?
Heat loss by conduction through a concrete wall as a function of ambient air temperatures ranging from -15 to 38°C is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 One-dimensional conduction. 2 Steady-state conditions exist. 3 Constant thermal conductivity. 4 Outside wall temperature is that of the ambient air.
Properties The thermal conductivity is given to be k = 0.75, 1 or 1.25 W/m•K.
Analysis From Fourier’s law, it is evident that the gradient, , is a constant, and hence the temperature distribution is linear, if and are each constant. The heat flux must be constant under one-dimensional, steady-state conditions; and are each approximately constant if it depends only weakly on temperature. The heat flux and heat rate for the case when the outside wall temperature is and k = 1 W/m•K are:
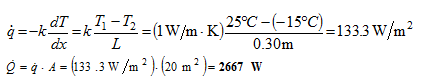
Combining Eqs. (1) and (2), the heat rate can be determined for the range of ambient temperature, ?15 ? ? 38°C, with different wall thermal conductivities, .
Discussion (1) Notice that from the graph, the heat loss curves are linear for all three thermal conductivities. This is true because under steady-state and constant conditions, the temperature distribution in the wall is linear. (2) As the value of increases, the slope of the heat loss curve becomes steeper. This shows that for insulating materials (very low ), the heat loss curve would be relatively flat. The magnitude of the heat loss also increases with increasing thermal conductivity. (3) At , all the three heat loss curves intersect at zero; because (when the inside and outside temperatures are the same), thus there is no heat conduction through the wall. This shows that heat conduction can only occur when there is temperature difference.
The results for the heat loss with different thermal conductivities k are tabulated and plotted as follows:
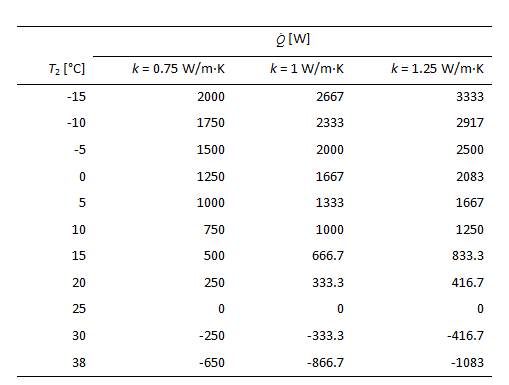
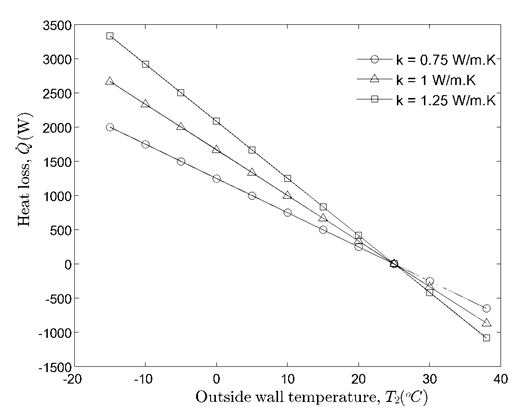
You might also like to view...
When dual voltage motors are used, the motor must be operated on the high voltage setting of the motor.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Explain the phenomenon of the photoelectric effect.
What will be an ideal response?
Most metal stairways _____.
a. require little or no fabrication b. solvent welded c. are welded d. extruded
? Identify and state the historical significance of "ethnic cleansing".
What will be an ideal response?